Generalist
Roles and tasks that involve applying knowledge from many domains in a flexible and dynamic way. For example, a hotel manager who deals with accounting, maintenance, operations and customer service in a single shift.Specialist
Roles and tasks that involve highly specific know-how such as an elevator technician who knows how to repair and maintain certain types of elevator. This includes trades such as electricians.Entrepreneur
An entrepreneur is an individual who creates new industries, business models, products, services and ways of doing things. This requires the flexibility of a generalist.Capitalist
An individual who puts capital and people to work. For example, a restaurant owner who employs dozens of people and generates value from capital such as buildings. This includes anyone who takes risks with their own money such as a farmer who puts land to work.Strategy & Planning
The process of forming strategy, making decisions and implementing. Includes roles such as executive management, project management and change management.Communications
Work that is primarily about communicating such as sales, customer service and advertising. This includes any role that is highly social.Healthcare
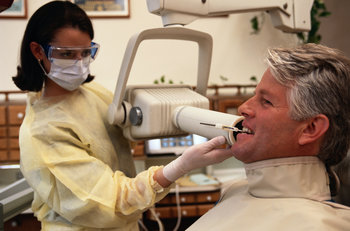
Any role in the healthcare industry. This involves the application of knowledge and has a human side that requires sympathy and ethics.Creative
The creation of nonobvious works. This includes areas such as art, design and craft where one work item may be extremely valuable and another worthless.Knowledge Work
Work that primarily involves creating, communicating, managing and applying knowledge. This includes diverse areas such as research, teaching and business operations.Professional Services
The services of recognized professionals such as doctors, dentists, lawyers and accountants.Management
Management is the process of directing and controlling teams, resources, processes and missions.Technical
The process of automating work including software development, technical specialists and technology operations roles.Administration
The bureaucratic practice of implementing policy, processes, procedures and standards. This includes any work that is standardized, repeatable and predictable.Manual Labor
Physical work that isn't particularly creative, specialized or social.| Overview: Work | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A productive pursuit that is intended to create value. | |
Related Concepts | ||