Procedures
Procedures are a series of repeatable instructions for accomplishing a task. A procedure is a simple type of process. Likewise, more complex processes can include multiple procedures. For example, a procedure for showing a guest to their room that is part of a greater check-in process.Procedure: Showing a Guest to Their Room
1. Take the guest's luggage.
2. Direct them to the elevator.
3. Direct them to the room.
4. Gently place the luggage on the luggage rack by the door.
5. Explain features of the room as required.
6. Answer any questions.
6. Tell the guest to enjoy their stay and depart by closing the door behind you while facing the guest.
1. Take the guest's luggage.
2. Direct them to the elevator.
3. Direct them to the room.
4. Gently place the luggage on the luggage rack by the door.
5. Explain features of the room as required.
6. Answer any questions.
6. Tell the guest to enjoy their stay and depart by closing the door behind you while facing the guest.
Checklist
A checklist is a process or subprocess that allows steps or tasks to be completed in any order.Checklist: Clean Guest Room
□ Change linens
□ Replenish toiletries
□ Collect garbage
...
□ Change linens
□ Replenish toiletries
□ Collect garbage
...
Business Rules
Business rules are formal logic that can be applied to work steps, tasks and activities. These are commonly included in processes.Procedure: Cleaning Entry to Guest Room
Knock twice and wait 40 seconds. Listen for activity.
If the guest is in the room but doesn't answer the door, call the room later by telephone.
If the guest is in the room, ask for permission to clean the room.
If the guest refuses cleaning, ask what time would be convenient.
If the guest is not in the room, enter to clean the room.
Knock twice and wait 40 seconds. Listen for activity.
If the guest is in the room but doesn't answer the door, call the room later by telephone.
If the guest is in the room, ask for permission to clean the room.
If the guest refuses cleaning, ask what time would be convenient.
If the guest is not in the room, enter to clean the room.
Workflow
A workflow is a process that includes both automation and human steps. For example, a check-in process at a hotel that includes human interaction, user input and computer code that performs tasks such as searching for a suitable room based on a customer request. Business rules are often automated in a workflow. The human steps in the workflow may be associated with procedures and checklists that are system validated to prevent human error.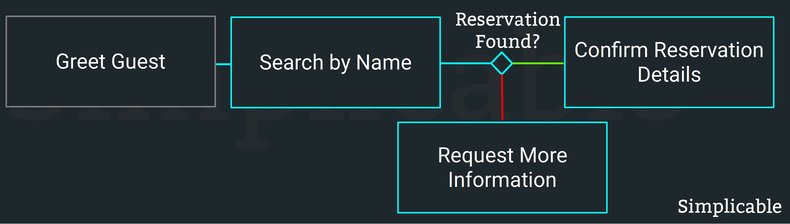
Automation
Processes can be fully automated with no human steps. For example, a cloud service that instructs solar panels to clean themselves as part of a maintenance process.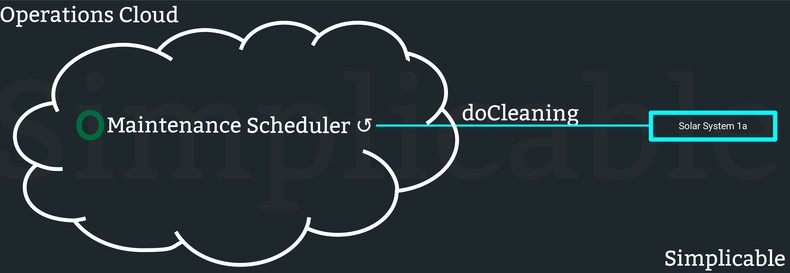
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is the repeated and ongoing process of measuring, changing and measuring again. Where changes are small, this is a process of optimization. Where changes are big, this is a process of experimentation. Continuous improvement can be applied to any type of work including processes themselves. For example, a designer who changes their creative process a little with each project to try to continually improve their productivity and results.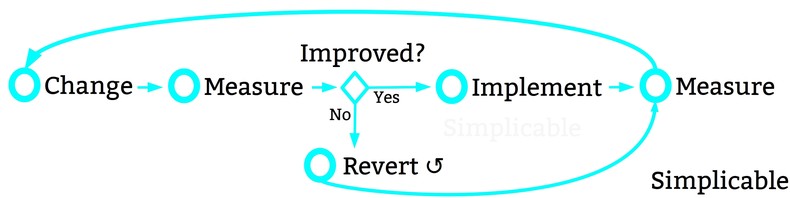
Management By Exception
It often doesn't make sense for a process to handle obscure conditions that rarely occur. Management by exception is the practice of implementing processes that handle most cases in a systematic way and allowing human decision making to handle exceptions. For example, an airline where a manager can override business rules implemented by a system where a customer has some reasonable argument as to why they are an exception to a rule.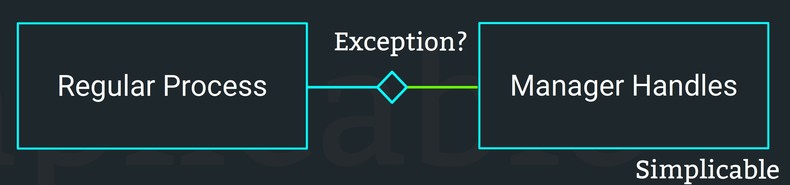
| Overview: Process | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Work that is systematic, managed and repeatable. | |
Related Concepts | ||