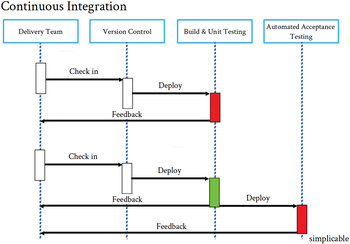
Continuous Delivery
The agile change manager shapes culture and stakeholder expectations to build a practice of continuous delivery whereby change is shipped within three to six weeks. This fights the common tendency to mark all requirements as "must have." For example, stakeholders may be required to impose a strict ordering on requirements such that a small chunk of work can be prioritized.Essential Complexity
Change managers represent the sponsor of change and work with stakeholders to keep things to their essential complexity. The idea is to ship value quickly and allow change to emerge. Stakeholders will tend to think big and may present ideas that represent decades of work. Change managers influence to shape such ideas into implementable chunks of value.Change Acceptance
Change is accepted at any time. This is most typically recorded in a backlog for the next cycle. However, work can be stopped and a cycle restarted at any time. This requires careful management and communication. The change manager plays a role in accepting and dealing with proposed changes to shelter the delivery team from constant chaos.Last Responsible Moment
A basic principle of agile change is that you don't overplan, overbuild or overthink. This is known as last responsible moment. For example, you don't need a 10-year product roadmap or a 5-year architectural plan. Decisions are delayed until they absolutely have to be made in order to allow for adaptability.Sustainable Development
Agile change isn't like a 3 year project where you may have intense periods of sacrifice that are completely unsustainable. A pace of change is established and sustained indefinitely. The change manager plays a critical role in setting this pace at a level that creates great value and provides a reasonable level of work-life balance for the delivery team.Issue Clearing
The change manager clears issues that are beyond the delivery team's control. This is done quickly and efficiently using influence and formal authority. In most cases, the change manager requires executive level authority and influence.Self-Organizing Teams
The agile change manager serves the delivery team and doesn't interfere with their work.Motivated Teams
Agile change requires talented, motivated teams that deserve trust. However, the change manager will manage performance issues and candidly offer teams feedback in a timely manner.Lessons Learned
With each cycle, improvements are identified for the next cycle. These improvements are sustained with knowledge, culture, processes and practices.| Overview: Agile Change Management | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The practice of leading continuous delivery processes whereby change is shipped within weeks. | |
Related Concepts | ||