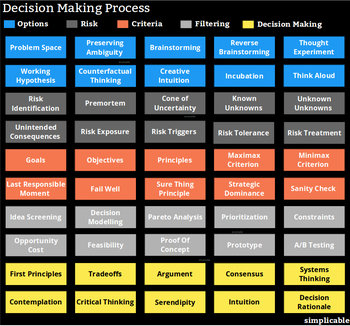
Decisions
An employee wants to quit to start a new business. They keep this information confidential from anyone tied to their current employer until they reach the day they are legally required to give notice. This keeps the employee's options open until the last moment. Days before the employee is planning to quit there is a market crash and a recession is predicted. The employee reconsiders the timing of their plan.Strategy
A firm develops a business plan to enter a completely new industry. The plan calls for a minimal investment that establishes a basic business model in a unique niche. Although the firm plans to dominate the entire industry with time, they take this small step to test the waters. They quickly fail and learn that there are competitive aspects of the industry that they had not considered. They review the risks of further investments and decide not to proceed.Design
A software team adopts the principle of last responsible moment when they switch to an agile software development methodology. They start releasing working code every few weeks as opposed to every few months. Each release only includes architecture that makes sense to the current functionality without a grand design for the future. The fast releases allow the team to see what works and rapidly improve their product.City Planning
A city decides that it is no longer appropriate to plan on 10 year cycles as challenges, technology and urban design methods are emerging too quickly. They develop a long term vision for quality of life and sustainability but keep planning to 2 years.| Overview: Last Responsible Moment | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The practice of leaving decisions, actions, designs and implementations as late as possible without narrowing options or incurring more risk. | |
Notes | Last responsible moment is a methodology that can't be considered a universal rule of strategy and decision making. In many cases, early decisions and designs have advantages. For example, cities may be designed to be highly resilient without need to identify some specific and imminent threat. | |
Related Concepts | ||