Economies of Scale
A firm that enjoys economies of scale has falling cost per unit as they produce more units. This gives large firms in an industry a lower unit cost than smaller competitors. Economies of scale can also apply to services or experiences as they scale up sales volumes. For example, a theme park finds that its cost per visitor is $60 with less than 5,000 visitors but falls to below $10 with 50,000 visitors or more.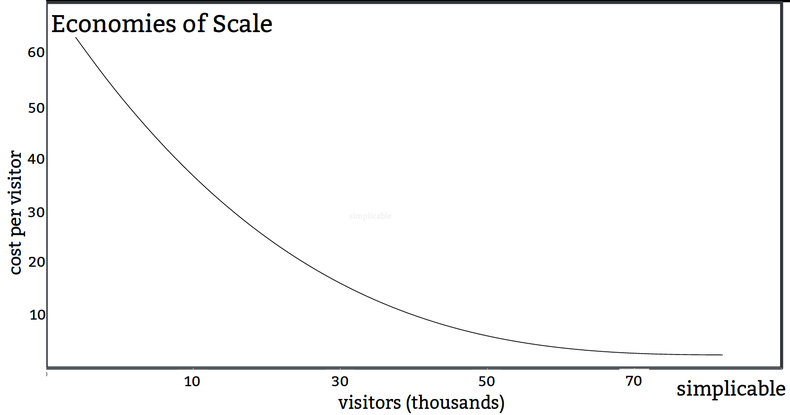
Comparative Advantage
Economies of scale can be applied at the level of nations. For example, a nation that produces 25 million tonnes of wheat a year may have far lower costs per ton than a nation that produces 1 million tonnes a year. A nation has a comparative advantage in wheat if its opportunity costs for producing wheat are lower than its trading partners.Diseconomies of Scale
Diseconomies of scale is a firm that faces increasing unit costs as is scales up. For example, a gold mine that can cheaply mine 5,000 ounces of gold each year with escalating costs to increase production further.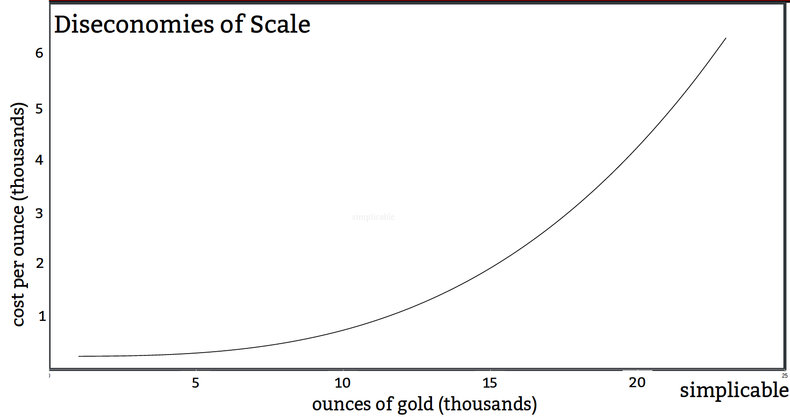
Constant Scale
In some cases, increasing sales volumes have no impact on your costs. For example, a small ecommerce seller who can only procure items at a fixed cost.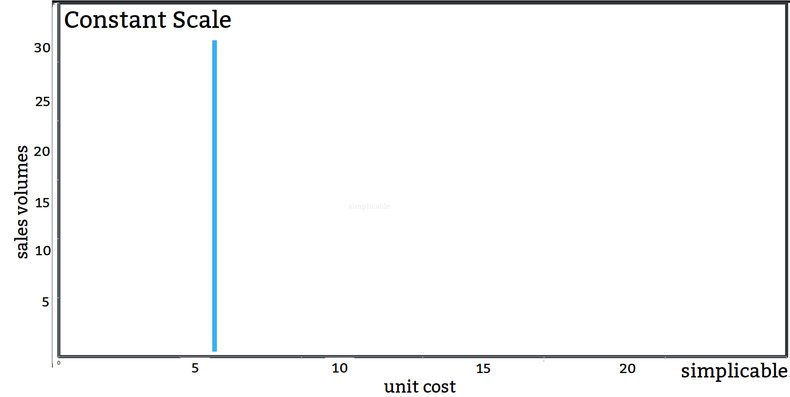
Niche Scale
In an industry with strong economies of scale it is difficult for a small firm to compete directly with larger firms as they have lower unit costs. One strategy to deal with this is to offer a niche product or service. For example, a small tea shop that has far higher units costs than local supermarkets thrives by selling rare, specialty and high quality teas both in their shop and on ecommerce sites.Premiumization
The other way for a smaller competitor to compete with a firm that enjoys greater economies of scale is to increase quality so as to charge a premium price. For example, a craft beer that incorporates local ingredients and traditions has a unit cost of $3 a bottle in a country where larger competitors have unit costs below $1. The craft beer competes on quality as they can't match the prices of the larger firms.| Overview: Scale | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The amount of production a firm achieves. | |
Related Concepts | ||