Workflow
Workflow is a class of software that orchestrates processes that include both automation and human work.Process Automation
A category of systems that are used to automate business processes. For example, an event processing platform for automating responses to events such as a customer inquiry or an error in a log.Service Automation
An approach to automation that packages work into automated or semi-automated services. For example, a service that can be used to generate customer bills.Analytics
Platforms for exploring data and building dashboards with an intuitive visual interface.Data Science
A broad and diverse category of software for managing data, discovering data and performing statistical analysis.Databases
Databases including those that can handle big data.Machine Learning
Machine learning, also known as artificial intelligence, is a class of software for automatically discovering and optimizing models that can be used to make decisions and perform work.Communication
Communication software such as email or a voice-over-ip telephone service for an office.Collaboration
Tools for working with others remotely such as video conferencing, virtual workspaces and document sharing environments.Office Productivity
Tools that knowledge workers use to create and share documents.Project Management
Software for managing projects.Media
Tools for producing or managing media. For example, a video editing suite.Content Management
Platforms for publishing and managing content and documents including internal and customer facing websites.Self-Service
Self-service functionality that allows customers, partners and employees to accomplish their goals without any help. For example, an ecommerce page that allows a customer to cancel an order without going through a customer service representative.Content Delivery Network
Content delivery networks, or CDNs, are platforms for delivering content from a data center close to each user to reduce latency.Edge Computing
Edge computing are platforms for executing code close to the where it is needed. This reduces latency and can be an efficient and resilient way to distribute work.Search
Tools for searching documents, media and data.Knowledge Management
Software for publishing, controlling, using and sharing knowledge, particularly documents.Infrastructure
Infrastructure is a catch-all term for systems and hardware upon which all other systems depend such as a cloud platform or database.IoT
Internet of things is the practice of connecting physical things and infrastructure to internet services. For example, a solar panel firm that manages a large number of systems remotely such that they can detect when a panel needs to be replaced.Robotics
Systems that automate physical work using autonomous or semi-autonomous machines.Integration
Systems that get things working together at the level of processes, events or data. For example, an ETL that is used to move data between systems.Batch Processing
Platforms for scheduling and executing regular automated jobs.Transaction Processing
Systems that execute transactions such as a purchase, stock trade or payment.Point of Sale
Systems for processing sales and customer service interactions from a store or other physical location.Contact Center
Software for processing customer interactions remotely using channels such as ecommerce, telephone, messaging and email.Payments
Services for transacting payments.eCommerce
Online stores and ecommerce platforms.eLearning
Remote learning services and tools.ERP
Enterprise resource planning is a class of very large packages of business software that try to offer everything that organizations in various industries need in one gigantic but unified package.CRM & SFA
Customer relationship management and sales force automation are very large information systems that try to offer everything that businesses need to manage sales and customer service processes.Marketing Automation
Marketing automation is a broad category of systems for marketing. This includes software that is focused on digital advertising and comprehensive platforms for marketing processes.Horizontal Software
Business software for a particular functional area such as a human resources or accounting platform.Vertical Software
Systems for a particular industry such as software for managing an electric grid.Consumer Software
It is increasingly common for large organizations to rely on the same devices, applications and mobile apps as consumers. This process is known as consumerization.Legacy Systems
Systems that are outdated such that they have a high risk of failure and are expensive to support. Firms often find it difficult to retire legacy systems and may continue to operate them alongside newer systems.DevOps
Platforms for delivering IT services such as a tool for managing the software development lifecycle.Service Desk
Software for managing requests to a service. Mostly used to manage IT services and systems.Resilience
Tools related to the resilience of an organization in areas such as business continuity, disaster recovery and backup & restore.Information Security
Systems related to information security such as an identity and access management service.Four Level Model
The four level model is an architectural concept taught in universities that structures information systems into four layers that correspond to the needs of workers, direct managers, senior managers and executives.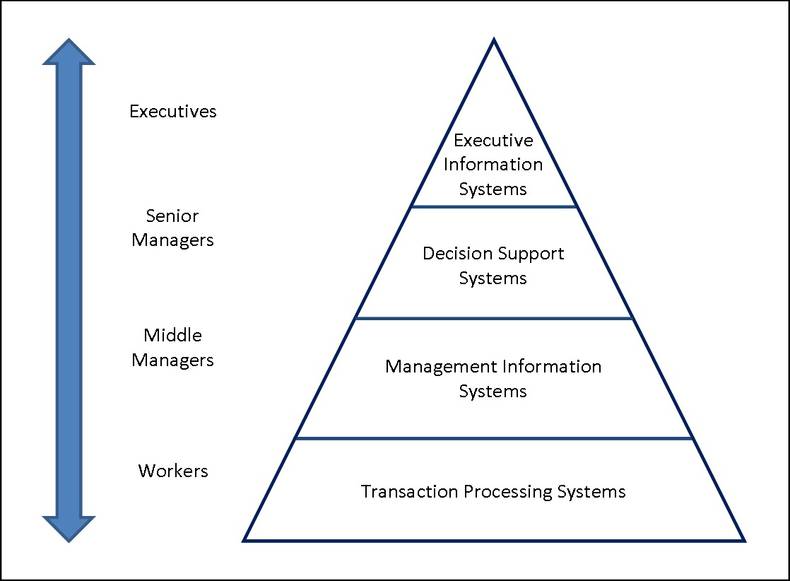
System vs Application
Generally speaking, the term system is applied to software that is primarily used for automation. Systems may have user interfaces but this isn't their primary function or value. Applications are tools that are centered around a user interface and servicing requests from users. Confusingly, the term information systems is commonly used to describe enterprise software including both systems and applications.Summary
The following are common types of information system:
Overview
Information systems can have user interfaces but also do work in a non-interactive mode to do things like build reports or execute transactions.
| Definition: Information Systems | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A class of software used by governments, businesses, non-profits and other organizations. | |
Related Concepts | ||