
Demand Curve
Demand is modeled as a curve that shows the quantity demanded by a market for a range of prices.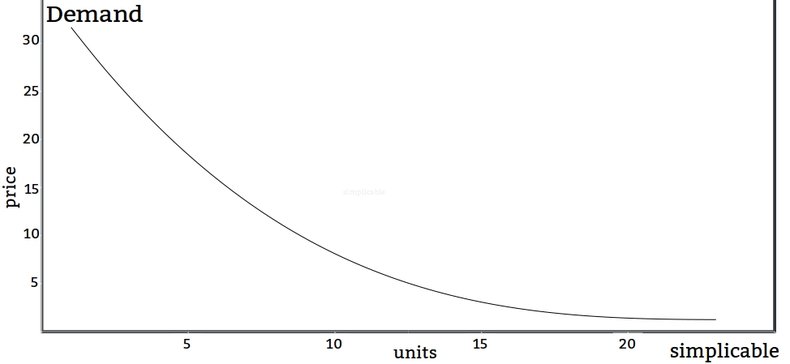
Law of Demand
The law of demand is a principle of economics that states that demand decreases as price increases and demand increases when price declines. In other words, all else being equal, price and demand have an inverse relationship. The law of demand means that demand curves always point down going from left to right.Equilibrium
The demand curve is typically modeled together with a supply curve that gives the quantity that market participants are willing to supply at each price level. Points where supply and demand curves intersect are known as market equilibrium.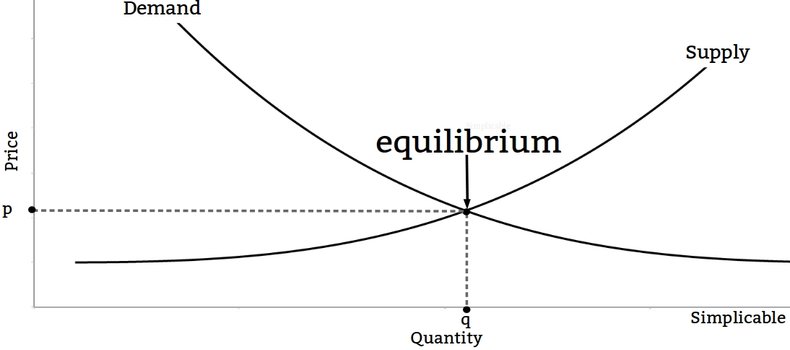
Elasticity
Price elasticity of demand is the percentage change in demand in response to a one percent change in price. These are almost always negative such that it is common to omit the negative sign. An elasticity of less than 1 is said to be inelastic. An elasticity of greater than one is said to be elastic. Firms achieve optimal revenue at a price where elasticity is exactly one. Where elasticity is greater than one, price increases result in less revenue.Notes
There are exceptions to the law of demand such as giffen goods that can experience more demand at a higher price.| Overview: Demand | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The quantity of a good, asset or other type of value that market participants are willing to buy at a price level in a given time period. | |
Related Concepts | ||





























