Assets | Brand image |
Brand recognition | Business processes |
Cash flow | Community engagement: |
Competitive advantages | Corporate culture |
Cost reduction | Customer loyalty |
Customer relationships | Customer satisfaction |
Designs | Economies of scale |
Employee satisfaction | Facilities |
Intellectual property | Inventions |
Know-how | Low environmental impact |
Market share | Operational efficiency |
Positive social impact | Product differentiation |
Product quality | Product variety |
Productivity gains | Profit margins |
Reputation | Resources |
Return on investment | Revenue growth |
Risk management | Service excellence |
Strategic partnerships | Systems |
Talented employees | Technologies |
Time-to-market | Trade secrets |
Capital
Durable goods that have productive potential such as a ride at a theme park.Assets
Physical assets such as land and digital assets such as data.Talent
The talent of a firm's employees. For example, a design firm with highly talented employees is generally more valuable than a design firm with untalented employees.Social Capital
The network of social connections a firm enjoys at a point in time. For example, a sales team that have a positive relationship with a firm's customers and target market.Know-how
The ability of the business to achieve productive and creative results. This is based on knowledge, talent, processes, procedures, controls and systems.Organizational Culture
The habits, norms, expectations and symbols of an organization. Formed by a firm's history and generally difficult to change. Used to explain how one firm may embrace change and creativity and another may resist change and be unimaginative as an organization.Intellectual Property
Designs, techniques, methods, formulas, trademarks and copyrights that are protected by law or trade secret.Brand Value
The value of a firm's brands based on factors such as brand recognition and brand image.Competitive Advantage
Capabilities that allow a business to outcompete in a competitive market. This can include processes, systems, tools, procedures, methods, formulas, knowledge, talent, designs and relationships.Products & Services
The economic value of products and services to customers.Quality of Life
The impact of a firm on the quality of life of employees, customers and communities. For example, all else being equal a firm that produces a great deal of pollution is less valuable to stakeholders than one that produces no pollution.Summary
The following are common types of business value: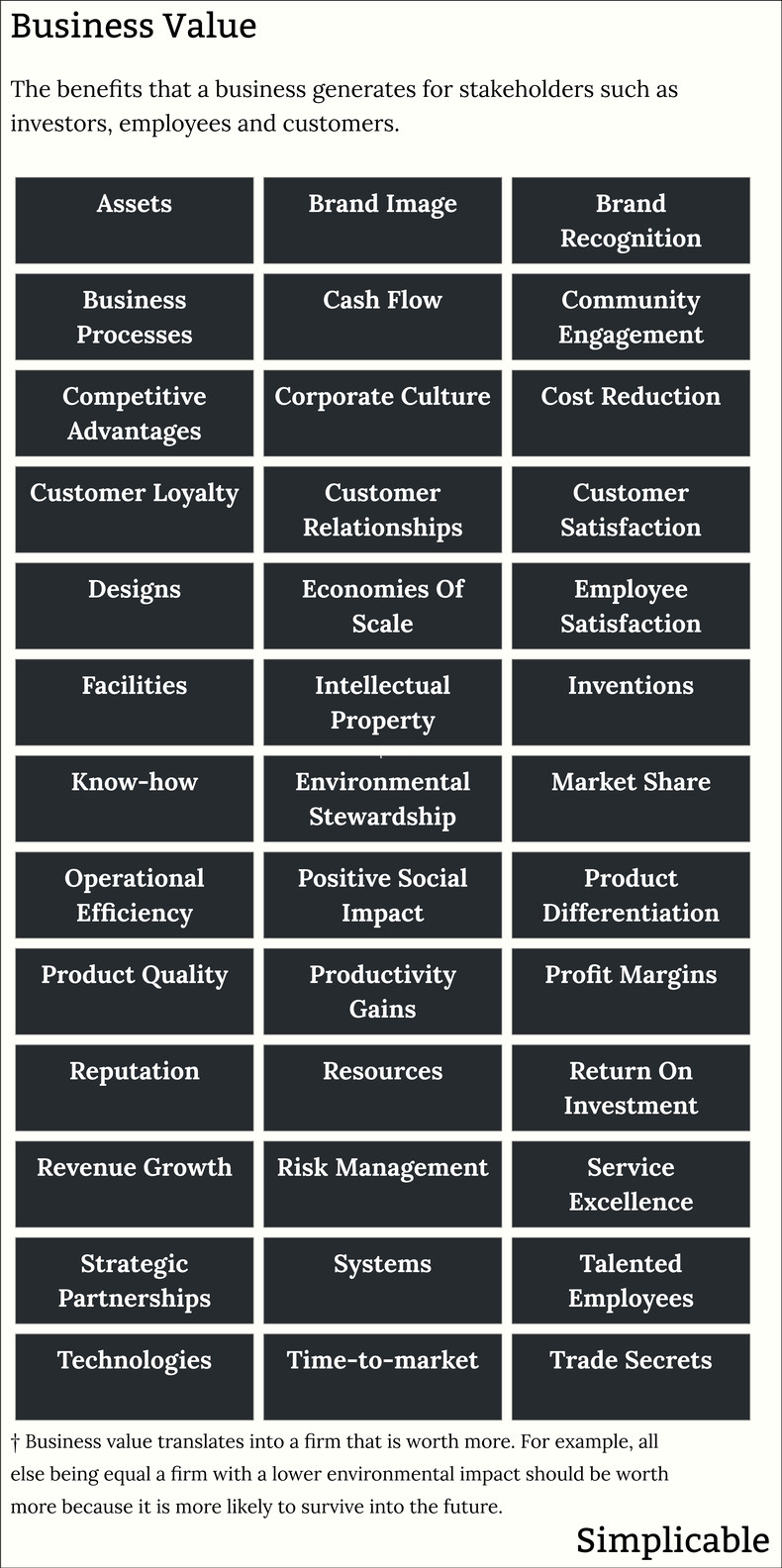
Overview
The value of a business to its stakeholder extends far beyond current revenue to the unique characteristics that will allow an organization to capture a valuable future position.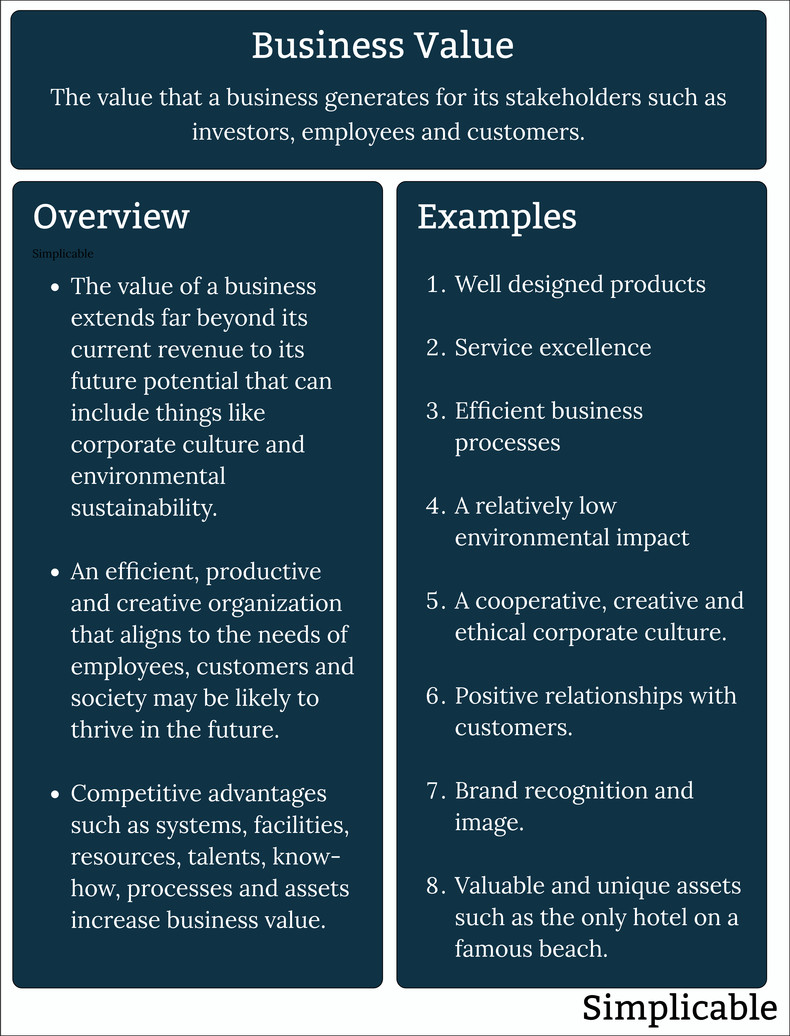
| Definition: Business Value | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The benefits that a firm generates for its stakeholders. | |
Related Concepts | ||