
Best Practices
A best practice is a best known method, process or procedure for a particular situation. These are commonly pitched by consultants who claim to know about best practices as a result of working for many different firms. It is also common for best practices to be captured by other third parties such as industry associations, government agencies or a professional body of knowledge. Firms commonly follow best practices when they have no interest in improving a business function but simply want reasonable results at a reasonable cost. For example, a space exploration company may have no interest in innovating in areas such as human resources.Standards
Standards are specifications of vocabularies, principles, methods, processes and practices that are developed by a process of agreement. The term implies that authorities on a topic are involved such as well known business leaders and academics. Standards are often useful in building capabilities that are compatible and equivalent across many organizations. For example, it is useful for firms to follow the same accounting standards so that investors can compare the performance of firms.Strategy
A strategy that seeks to emulate a competitor as opposed to leading an industry. For example, an IT firm that closely copies the products and services of competitors without any prospect of surpassing the competition to establish a competitive advantage.Outsourcing
Generally speaking, functions that are outsourced can not represent a competitive advantage because the partner typically offers the same services to many firms. For example, a real estate agency may outsource its IT functions if this is not viewed as relevant to its core business.Out of the Box
The purchase of the capital and services that aren't customized to have any advantage over the competition. For example, a sales team that uses a sales automation service that is commonly used in its industry.Spending
Firms may benchmark their spending in areas such as advertising, information technology and human resources against the competition. In many cases, the firm doesn't seek to have lower spending or higher spending but instead seeks spending parity. For example, a brand with high market share and brand recognition may seek to spend the same amount on advertising as a close competitor. This is done because a firm can't improve its brand recognition beyond the point that almost the entire market recognizes the brand. As such, the brand simply needs to defend this position by spending as much as the most threatening competitor.Overview
Competitive parity is a situation where you are seeking to match the performance of your competition.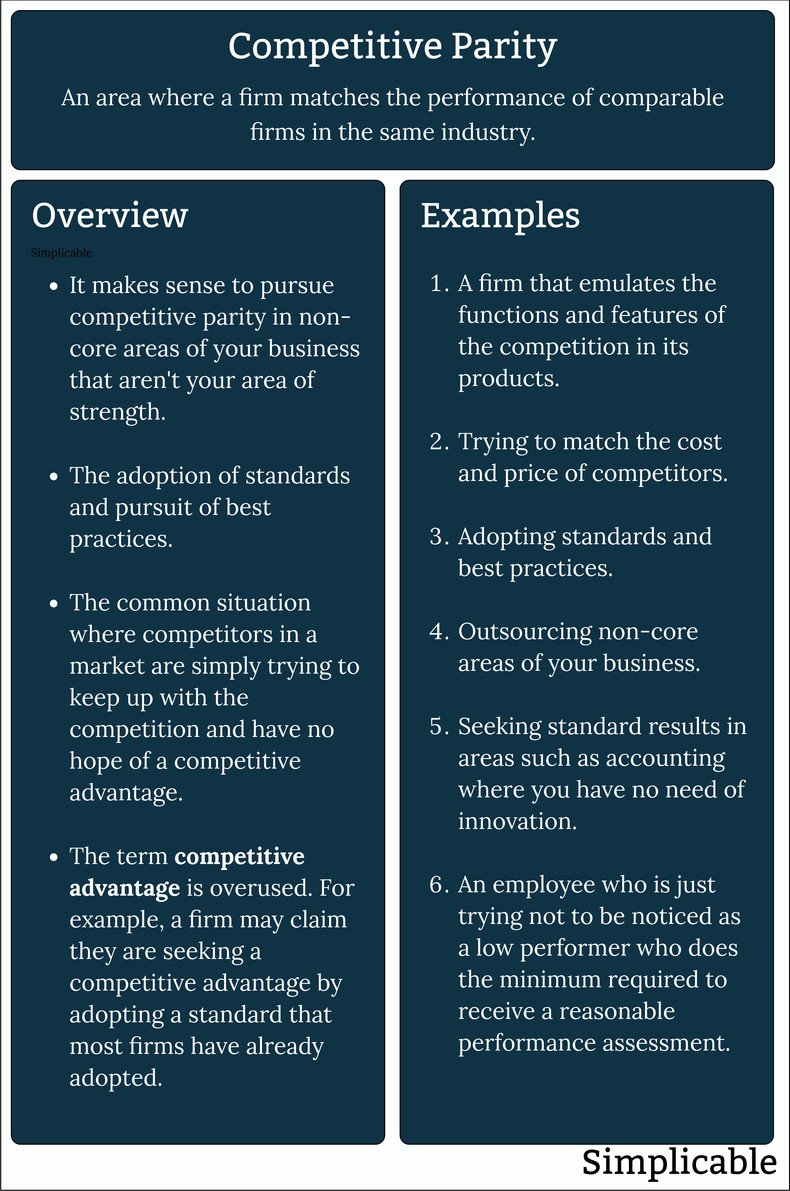
Notes
Firms tend to use the term competitive advantage even when their intent is really just to catch up or equal the competition in a particular context. However, it can be useful to be candid about the areas where you don't need to outcompete or areas where you have no hope of outcompeting.| Definition: Competitive Parity | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A goal to reach the same level of performance as a competitor or industry average. | |
Related Concepts | ||
































