
Demand
Demand for media such as television or newspapers. For example, a nation that has relatively fixed demand for television shows in a year based on the average hours spent watching television.Supply
Supply of media such as the number of television shows released in a year in a particular nation.Pricing
Pricing of media such as customary prices and sticky prices for ebooks. For example, sales volumes for an ebook may drop significantly when a price is set above a customary price such as $9.99.Attention Economics
Models for valuing the attention of customers. For example, the value of getting a particular ad in front of a particular customer when they are shopping for a digital camera.Markets
The economics of media markets such as modeling prices for advertising based supply and demand.Network Effect
The network effect is the tendency for certain services to be more valuable to each customer when the service has many customers. For example, a social media site that is valuable to users because they can find their friends, family and colleagues on the site. In some cases, a social media site could be badly designed and operated but still be valuable to customers simply because it has so many users.Six Degrees of Separation
The mathematics behind the common observation that word of mouth is critical to the success of media such as television shows, films and music. Six degrees of separation predicts that if you create a social graph of the population of the planet that most people are separated by no more than 6 connections. Therefore, media can quickly gain an audience on a global basis when people share recommendations with friends.Rule of Three
The theory that in a competitive market, three firms emerge with most of the market share. This is a pattern that is reported in many industries, including the media industry. For example, a nation may have three major newspapers or three major television networks. According to the theory, a nation with five or six major television networks is likely to undergo further consolidation.Information Pollution
Information pollution is inaccurate, misleading or low quality information. For example, a newspaper that reports dramatic stories that aren't entirely true in order to obtain more readers. This can be viewed as an economic bad that is created by intensive competition without ground rules such as industry norms or government regulations.Opportunity Cost
Opportunity costs are the trade offs that customers make with constrained resources such as time and money. For example, a student who has two hours after completing their homework to either read, play video games, watch television or surf the internet.Substitute Goods
The ability of customers to substitute one good for another. Generally speaking, most media are perfect substitutes. For example, an audience can substitute one television show for another or one book for another.Scarcity
Media is an unusually non-scarce resource. For example, a television show can be easily distributed to an audience of millions using broadcast media or internet streaming. This could be scaled to billions of people if the media were popular enough. This can be compared to a scarce resource such as gold whereby it is extremely costly or impossible to quickly scale up production.Competitive Advantage
Media is an extremely competitive industry because demand is fixed, media is non-scare and media goods are easily substituted. For this reason, competitive advantages are required to survive in the media industry. For example, a newspaper that breaks stories before the competition or a television show that is more entertaining than average.Globalism & Protectionism
Media easily crosses borders and media organizations such as film production companies benefit from the ability to distribute their products on a global basis. However, media is also subject to protectionism as it is seen as an element of a nation's culture. For example, a nation may subsidize its creative industries in order to protect its culture such as language and traditions.Summary
The following is an overview of media economics with a few additional examples.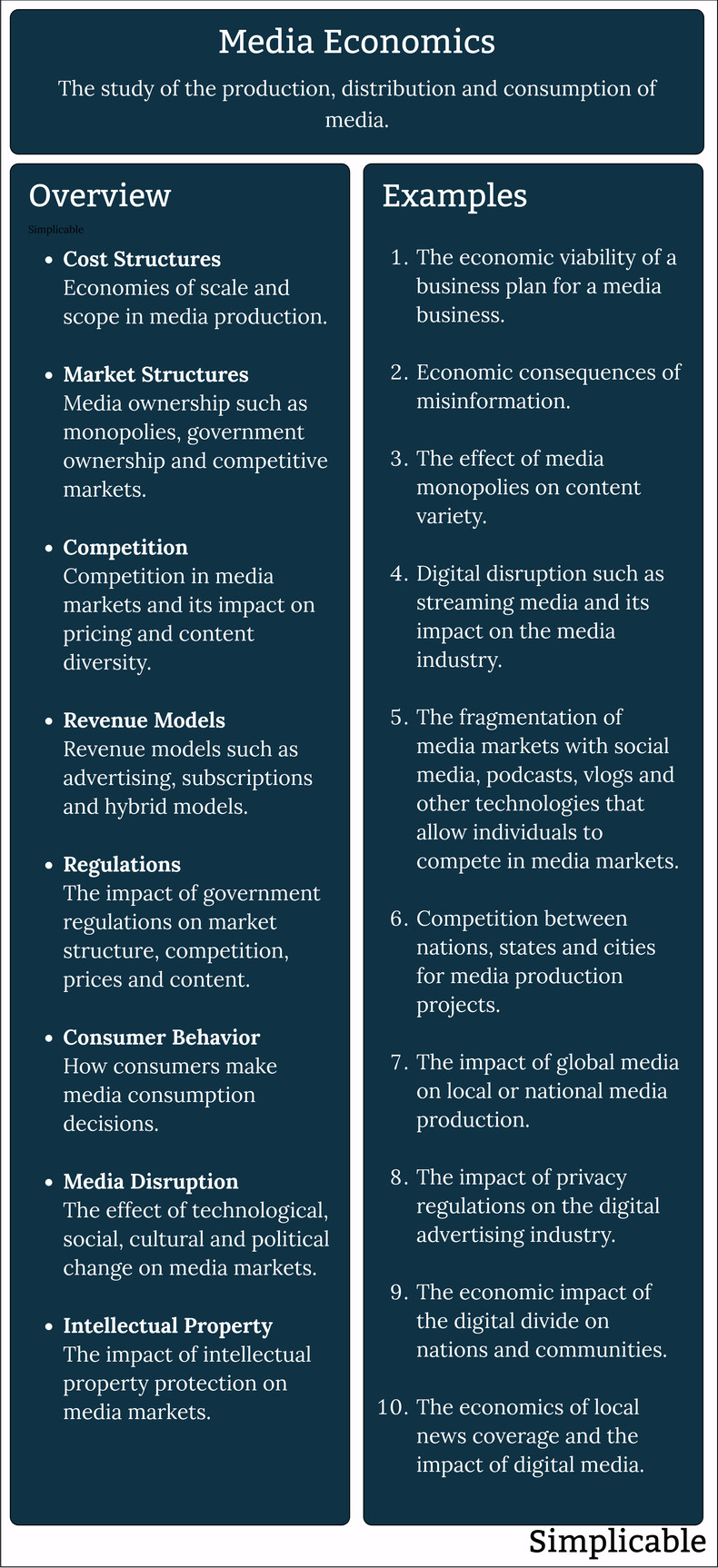
| Overview: Media Economics | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The science of modeling value creation, competition and markets in the media industry. | |
Related Concepts | ||


































