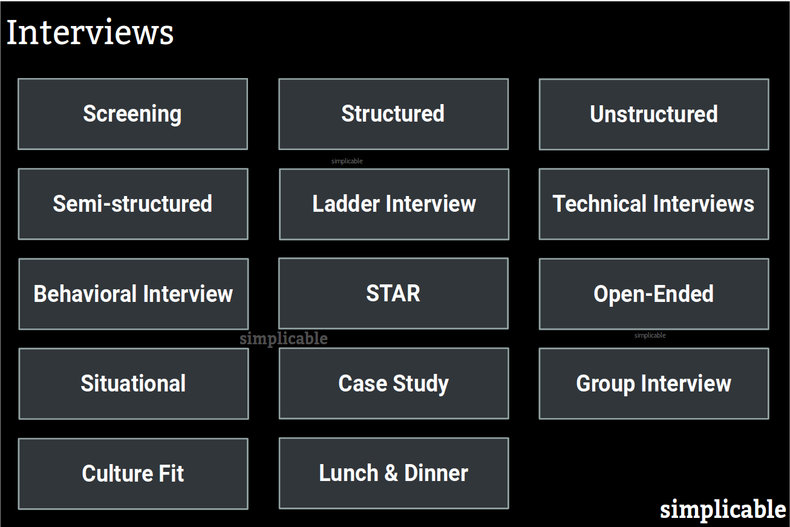
Screening Interviews
A quick interview, often by telephone that seeks basic qualifying information from a candidate in areas such as education, experience, availability and salary expectations. Screening interviews typically lack depth and the interviewer may take the candidate's answers at face value. A screening interview is simply intended to see if a candidate's stated capabilities match a firm's needs.Structured
Structured interviews are based on predefined questions. In some cases, follow up questions and other dynamic conversations are discouraged. Structured interviews are typical of bureaucratic organizations that are seeking to standardize their interviews to avoid bias. This prevents an in-depth exploration of the talents of each individual.Unstructured
Unstructured interviews are unique conversations that may explore one area at significant depth. For example, an interview that goes off on a tangent about artificial intelligence. This may be useful if you want to make sure a candidate is an expert in a particular area.Semi-structured
It is rare for an interview to be purely structured or unstructured. In many cases, an interview is based on a loose structure that is allowed to flex. For example, a small number of predefined opening questions with spontaneous follow up questions representing the bulk of the interview.Ladder Interview
An interviewing technique borrowed from market research whereby interviewers ask several levels of follow-up questions on the same topic to dig deep into each area. For example:How do you deal with angry customers?I am able to stay calm to try to discover the root cause of their dissatisfaction. Armed with this information, I try to solve the problem in a professional and friendly way.Can you give me an example where you did this?Sure, when I was working at _________ hotel the city increased the occupancy tax on hotels and we had to collect these extra fees from customers. Customers were accustomed to taxes being included and several customers got quite upset about this. I calmly explained that the city had increased the taxes with little notice for us to update our systems and explained that these taxes aren't optional for us.Did this approach work?In most cases, customers were forgiving after learning the reason behind the charge.What did you do when they were not satisfied with your explanation?In several cases, I got approval from a manager to refund an amount equal to the tax because the customer was still very unhappy.Do you think this was a good approach?Sure, the customer is always right. Hotels can't afford bad reviews so a small refund like that is worth making a customer happy.
Technical Interviews
Technical interviews probe a candidates understanding of a technology such as an application, system, programming language, API or platform. These may use ladder interviewing techniques to explore the candidates understanding at several levels such as the architecture, implementation and business level. This prevents candidates from memorizing answers and spitting them back out.Behavioral Interview
A behavioral interview explores a candidate's experience with questions such as "tell me about a time you..." This is a popular format for interviews as it explores a candidate's past performance related to a job.STAR
STAR is a structure for behavioral interviews that explore four elements for each experience area: situation, task, action and results. Situation is a business scenario, task is the candidate's role in the scenario, action is a description of what the candidate did and results are business outcomes. STAR is typically used to ask follow up questions in a behavioral interview until the candidate has covered each area. STAR is also a useful format for answering behavioral interview questions because this is generally what interviewers are looking for in a response. For example:Can you tell me about a time you improved a business process?Sure, at ________ telecom we had a provisioning process that basically does everything that is necessary to activate a service for a new customer. My role in the process was to active the customer's billing account so that they could be billed. There was always a drive to speed up this process because it took 14 days and this was a customer satisfaction issue. Part of this 14 days was 2 days for the billing account set up that was my responsibility. For some reason, this was being done after all the technical work had been completed to avoid billing the customer too early if a technical problem was encountered. I improved this process by completely setting up the customer from day 1 with an inactive flag. When the technical work was completed, all we had to do was change this flag to start billing the customer. This allowed us to reduce the provisioning time to 12 days from 14 days which helped close more sales and improve customer satisfaction.
The answer above outlines a complete business problem and clearly shows a measurable improvement directly contributed by the candidate. It also shows the candidate is aware of the business impacts of their work.Open-Ended
Open-ended interview questions require an expansive answer and test a candidate's domain knowledge such as their understanding of a business, industry or technology. For example, "how will information technology be different 10 years from now?"Situational
Asking a candidate how they would respond to hypothetical situations. This is particularly useful if a candidate doesn't have much experience or if the job has unique elements.Case Study
Asking a candidate to conduct an in-depth problem solving exercise based on a real or hypothetical problem statement. This has several common variations:Professional Abilities | Applying specific domain knowledge to solve a problem such as a software developer who is asked to design an algorithm. |
Convergent Thinking | Convergent thinking is the ability to find the right answer to a problem. For example, a question that resembles an IQ test that asks a candidate to apply logic. |
Divergent Thinking | Divergent thinking is the ability to invent new things. For example, a case study that asks a candidate to invent a completely new product that meets a stated set of customer needs. |
Systems Thinking | Systems thinking is the ability to think through the end-to-end impact of things to find elegant solutions to complex problems. For example, a management consulting case study that asks a candidate to solve a socio-economic problem for a government. |
Group Interview
An interview of more than one candidate at the same time. This is often a case study that has candidates discuss solutions to a problem as a team. A group interview can be used to explore abilities such as leadership, collaboration and cultural capital. For example, a candidate may show that they are personable, outgoing and good at leading a collaborative exercise in productive directions.Culture Fit
Culture fit interviews generally involve a single candidate meeting with two to five members of a team to see how things go. It is common for the hiring manager to observe this to see how the candidate handles the different personalities on a team.Lunch & Dinner
Culture fit interviews may have a social element such as a lunch or dinner with a number of team members. This type of interview may only be offered to short listed or preferred candidates who are somewhat likely to win the offer. Lunch and dinner interviews are informal. Candidates often find these challenging nonetheless as it can be difficult to balance a need to appear social and fun with the need to sell your professional abilities. For example, alcohol is certainly a bad idea for the candidate but this is also considered a social element of a meal in many cultures.| Overview: Interviews | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A conversation between representatives of an organization and a job candidate designed to evaluate the candidate's suitability for a job. | |
Related Concepts | ||