Languages
The ability to speak, write and comprehend a language.Technical Skills
The ability to use and administer technologies such as operating systems, networking tools, applications, systems and devices. For example, a customer service representative who is familiar with several customer relationship management platforms.Software Development
The ability to write code and participate in a software development lifecycle. These are basic skills and it tends to be more difficult to measure more advanced software development skills such as software architecture and design. Generally speaking, design is a soft skill as it is creative in nature.Machines, Vehicles & Equipment
The ability to operate, configure or maintain machines, vehicles or equipment including computing hardware.Science
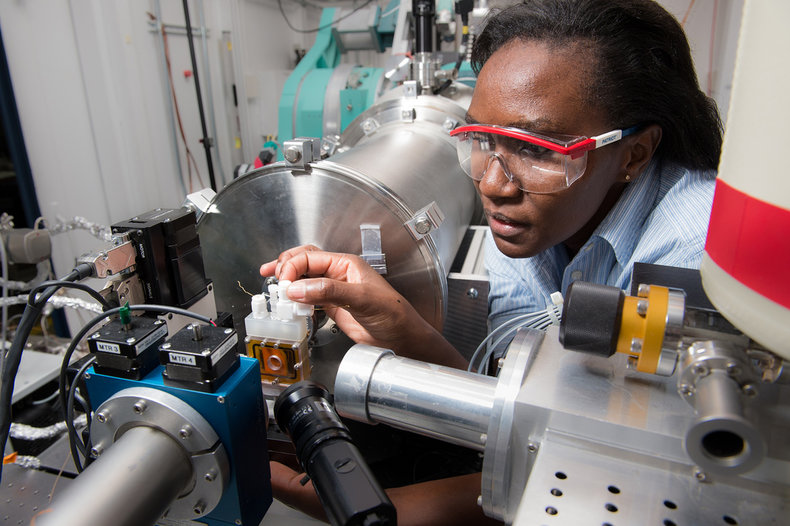
Science related knowledge and abilities are considered hard skills that can be measured with tests. For example, an individual with an undergraduate degree in physics from a well known university and a high grade point average has hard evidence of their scientific knowledge and ability to apply that knowledge to problems.Mathematics
Mathematics and related skills such as statistical analysis.Education
Completed education is often considered evidence of hard skills. This is particularly true for degrees that are considered difficult to obtain that involve extensive testing of applied problem solving abilities. For example, an engineering or computer science degree is certainly a hard skill that is described with professional designations such as engineer and computer scientist.Occupational License
Any profession that requires a license to practice such as doctor, lawyer or pilot is considered a hard skill due to the level of testing that is required to obtain such licenses.Professional Certifications
Professional certifications that are considered difficult to obtain are considered hard skills, particularly if they are in high demand by employers.Notes
Most hard skills aren't completely testable. For example, it is common for project managers to be certified in a project management body of knowledge. However, the real skills that correlate strongly with success as a project manager are soft skills such as industry experience, communication and influencing.As hard skills are testable, employers tend to require candidates to provide proof of hard skills. For example, some employers will require project managers to be certified even if they have been managing projects for many years.The term hard skill implies a skill that is in high demand in the labor market. For example, it may be possible to test your knowledge and ability to apply philosophy but this isn't typically considered a hard skill due to a lack of interest from employers.| Overview: Hard Skills | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A category of ability that can be measured with standardized testing. | |
Related Concepts | ||
































