Product quality | Service excellence |
Talented employees | Brand recognition |
Financial resources | Operational scale |
Online presence | Brand reputation |
High market share | Diverse range of products |
Low costs | Know-how |
Technologies & tools | Industry experience |
Industry relationships | Customer base |
Partnerships | Operational efficiency |
Fast turnaround time | Local presence |
Global presence | Revenue growth |
High productivity | Marketing prowess |
Low debt | Efficient supply chain |
Proprietary technology | Efficient processes |
Product designs | Intellectual property |
Facilities | Locations |
Fast time to market | Customer experience |
Product functions & features | Adaptability to change |
Regulatory compliance | Ethical business practices |
Environmental footprint | Responsive to market trends |
Talent
Talent such as a architect who produces more creative and valuable designs than their peers.Knowledge
Knowledge such as an organic tea farmer who knows how to use unique companion plantings to increase yield, decrease cost and improve quality.Productivity
Productivity is how much you produce in an hour of work. For example, a talented software developer who produces more code than an average team of 12 people.Efficiency
Efficiency is how much output you create for each unit of input. For example, a data center company in a cool climate that uses far less power for cooling than most of the competition.Scale
Producing at greater scale than the competition to reduce unit costs. For example, a cosmetics company that produces millions of units a week may have a significant cost advantage over a competitor that produces thousands of units a week.Speed
The ability to do things quickly including the turnaround time of business processes. For example, a bank that completes most transactions in seconds has an advantage over a bank that takes 3 business days to do anything.Change
The ability to change to achieve strategy. For example, a manufacturer that implements more than 10,000 improvements to IT systems and tools each year when a major competitor delivers less than 100 improvements a year.Innovation
The ability to do more than copy the competition by finding new business models, methods and products that are non-obvious and valuable.Business Capabilities
Business capabilities such as an engineering firm that can accurately measure project risk where the competition often develop poor risk estimates.Distinctive Capability
An ability to do something of value that is unique in the market. For example, an architect who is a master of daylighting techniques such that they can design large structures that require little or no electric lighting during the day.Bargaining Power
Bargaining power such as a large ecommerce company that is able to push delivery companies for steep discounts that aren't available to smaller competitors.Finances
Financial position such as a technology company that generates large amounts of cash flows from operations. This can be used to do things such as preventing competition by purchasing all the promising startups in your industry.Location
Location such as a software sales team that is located in a financial district close to major customers when the competition is out in the suburbs.Brand
Brand recognition and brand image are common types of competitive advantage. For example, a fashion brand that is perceived as luxury and premium such that there is social status attached to products.Quality
Quality is the fitness for purpose of something. For example, a baseball bat design that is lighter and stronger than alternatives on the market due to the use of a new composite material.Barriers to Entry
Controlling something or knowing something that makes it difficult for new entrants to challenge you. For example, a railway that owns land stretching great distances through urban areas that would be impossible to purchase today without an act of government.Technology
Superior systems, applications and machines such as a train manufacturer with an automated assembly line that reduces costs, disruptions and quality issues.Infrastructure
Access to superior infrastructure. For example, a data center directly connected to a major internet backbone may have a latency advantage over a data center that has several hops to reach a backbone.Relational Capital
Relationships such as an information security consultant who knows more people in the industry than their competition.Reputation
Reputation such as an energy company with a reputation for environmental stewardship, quality products and responsible management of resources. In some industries, a positive reputation is somewhat rare such that is potentially a valuable asset.Diversification
Offering a broad range of products and services can protect a firm from price swings and other disruptions to an industry. For example, an electronics manufacturer that produces hundreds of products may be able to survive a price war in one product category that takes out competitors that are less diversified.Positioning
A valuable position in a competitive market. For example, the solar panel company that makes the most efficient and durable product.Network Effects
Some services become more valuable as more people use them. For example, the value of a social media tool mostly comes from the number of people who are using it.Customer Service
An established ability to develop and sustain positive relationships with customers by being helpful, diligent and friendly. In some cases, firms struggle for decades to try to improve customer service without much success. As such, a positive service culture can be an extremely valuable asset.Customer Experience
The end-to-end customer experience offered by a business. For example, a restaurant with diligent service, a stimulating environment, beautiful decor and delicious food.Resilience
The ability of a business to survive stress and problems. For example, an IT consulting firm that learns from unhappy clients and failed projects verses one that pretends every engagement was a success.Summary
The following are common types of SWOT strengths: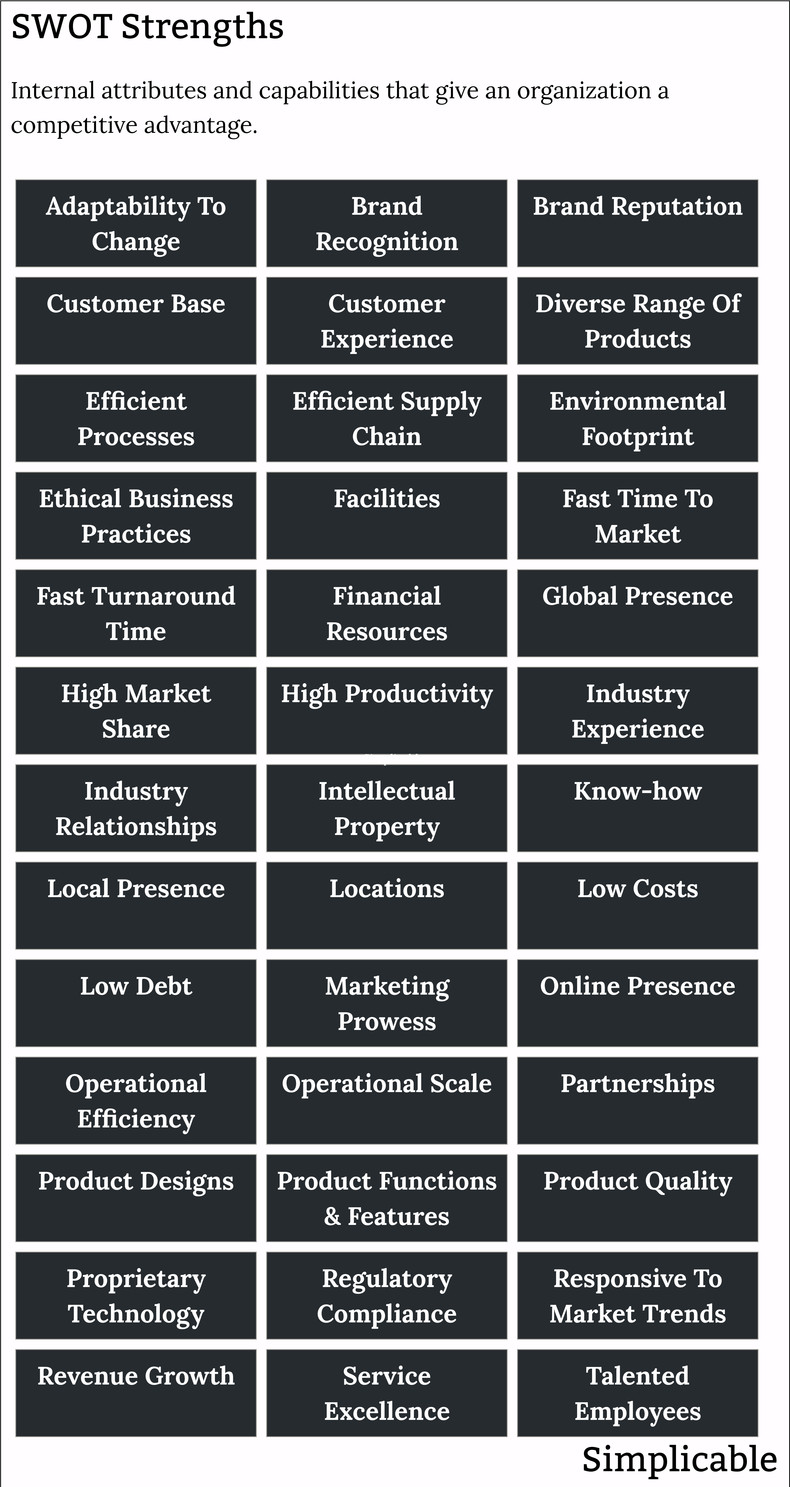
| Overview: Strengths (SWOT) | ||
Type | ||
Definition | An advantage over the competition in the current environment. | |
Related Concepts | ||