
Inconsistent strategy & direction | Poor alignment of goals across teams |
Limited financial resources | Inefficient resource allocation |
High debt levels | High operating costs |
Limited product range | Inefficient processes |
Overly complex processes | Negative customer reviews |
Declining sales | High customer attrition |
Inadequate loyalty programs | Dependence on a few customers |
Dependence on a single product | Dependence on a partner |
Dependence on key employees | High employee turnover |
Employee absenteeism | Overreliance on a single supplier |
Slow decision-making | Low employee morale |
Low productivity | Insufficient product quality |
Poor branding | Low brand recognition |
Inconsistent branding | Excessive bureaucracy |
Lack of creativity | Failure to meet deadlines |
Failed projects | Resistance to change |
Unreliable vendors | Aging products |
Outdated technology | Poor system usability |
Poor product usability | Poor cost control |
High overhead costs | Inadequate risk management |
Ineffective marketing campaigns | Inadequate employee training |
Uncompetitive prices | Inconsistent pricing |
Difficulty in scaling operations | Inefficient tools |
Inconsistent policies | Compliance issues |
Customer service issues | Supply chain issues |
Difficulty recruiting talent | Unclear product positioning |
Inadequate quality control | Inaccurate forecasts |
Poor inventory management | Cybersecurity issues |
Data quality issues | Negative environmental impact |
Unresponsive to customer feedback | Poor customer support |
Slow turnaround time for customer requests | Delayed customer orders |
Insufficient metrics, reporting and visibility | Overfocus on a particular metric |
Lack of standards | Lack of processes |
Excessive cost cutting | Reactive approach to problems |
Overemphasis on short-term goals | Lack of collaboration between teams |
Customer Experience Weaknesses
Issues with your customer experience such as unreliable products and long wait times for support.
Employee Related Weaknesses
Employee related weaknesses such as an advertising team that lacks training and experience with digital advertising.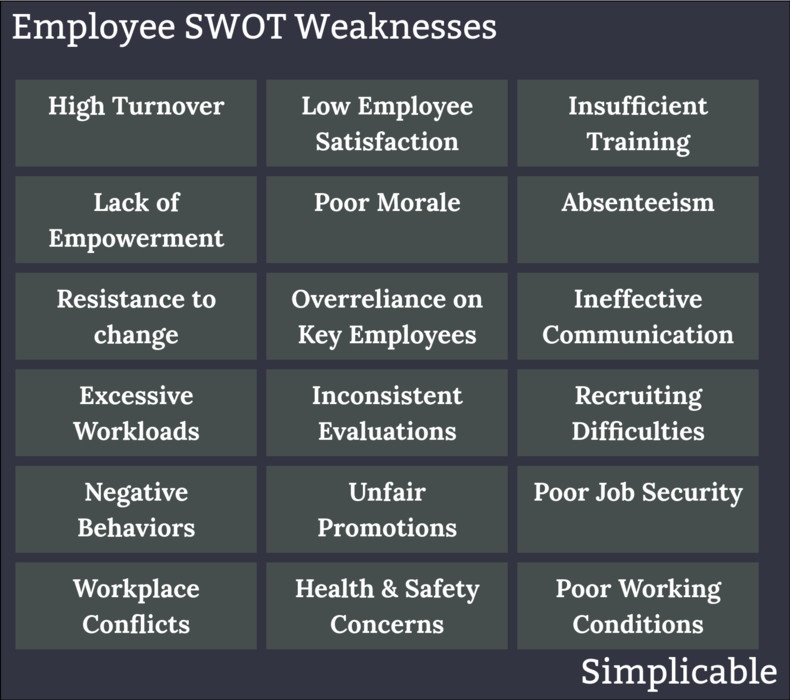
Operational Weaknesses
The efficiency and quality of your operations. For example, a speaker manufacturer that produces a large number of quality control failures due to aging equipment.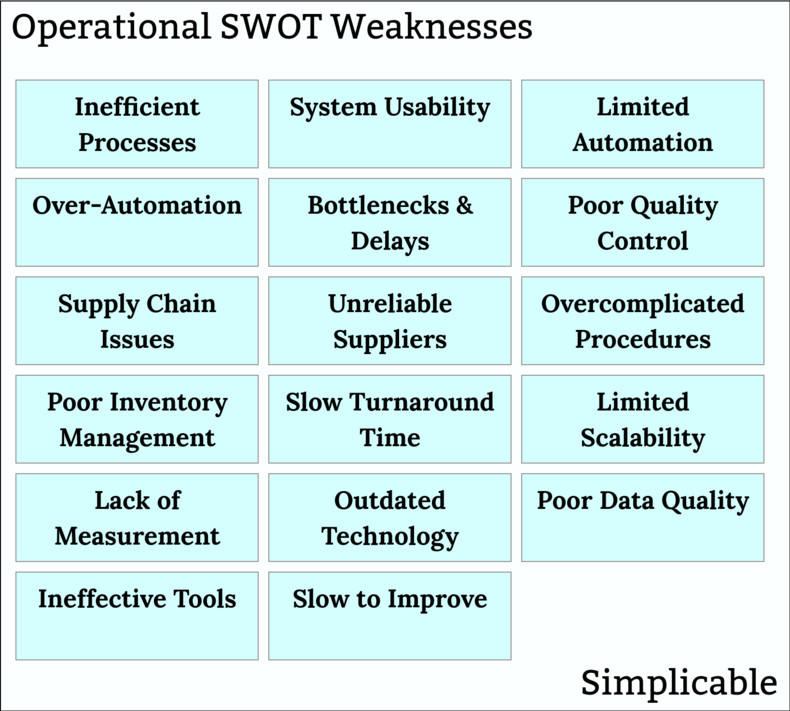
Management Weaknesses
Shortfalls of strategy, planning, direction and change. For example, projects that conflict and fail to align across teams.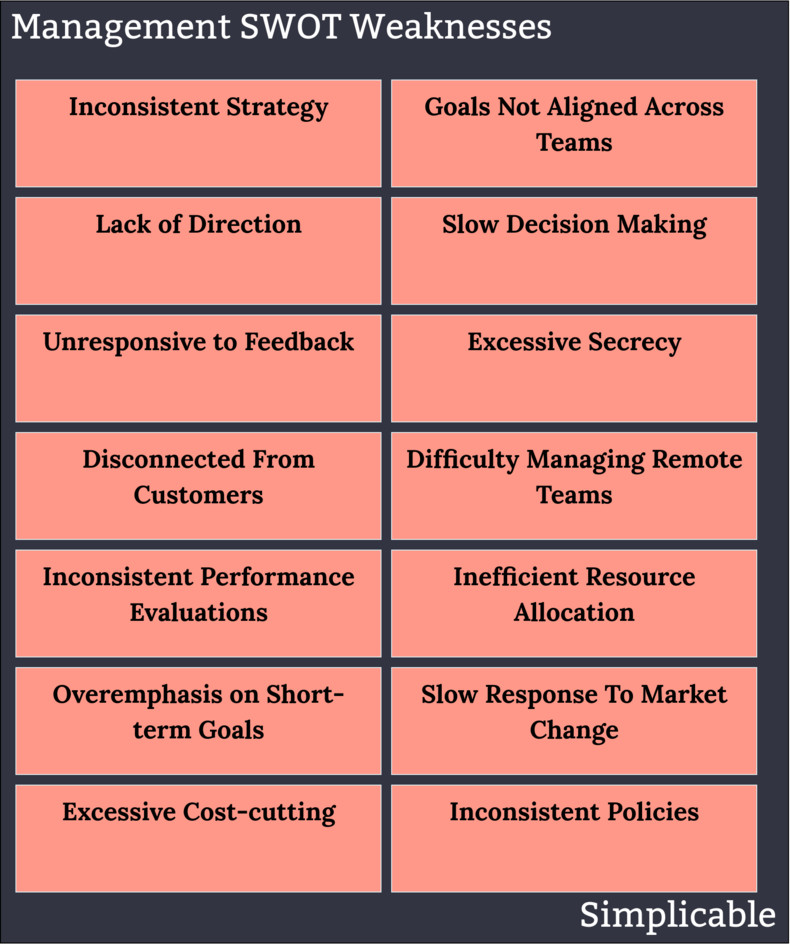
Financial Weaknesses
Financial weaknesses such as higher overhead or unit costs than the competition. For example, an organic farmer who produces apples for $8 a bushel when the average competitor achieves a cost of $7.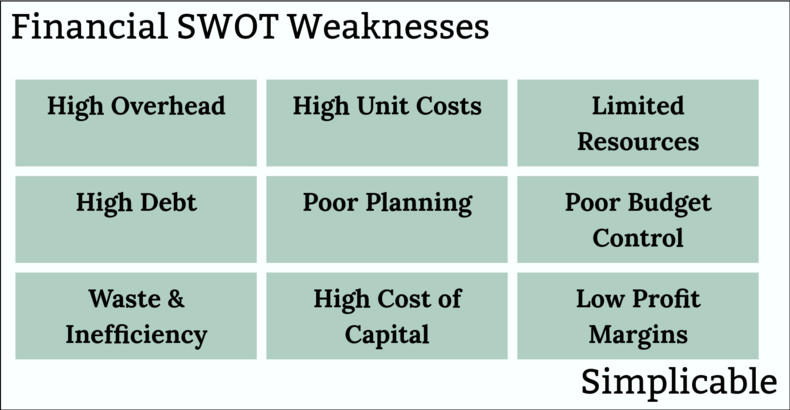
Knowledge
A lack of know-how such as a solar panel manufacturer that doesn't know how to make their products as durable as the competition.Prices
Prices and price structures that aren't as attractive as the competition. For example, a telecom company that charges for bandwidth when the competition offers attractive unlimited plans.Supply Chain
Suppliers and supply chain competition. For example, an ecommerce company that requires at least 3 business days to deliver an order when a competitor can deliver in 24 hours.Distribution
Your ability to reach the customer to sell to them and deliver your obligations. For example, a sushi restaurant that is 4 blocks from a busy shopping street when a competitor has three locations on the street itself.Brand
Poor brand recognition and brand image as compared to competitors. For example, an electronics manufacturer with a high quality product but a brand that the target market do not recognize such that they are hesitant to buy.Customer Service
Customer service shortfalls such as a firm that doesn't measure customer satisfaction at the interaction level such that employees who consistently displease customers aren't detected as low performers.Customer Relationships
Customer relationship issues such as a sales team that has seen significant turnover such that sales representatives are strangers to major accounts.Quality
The quality of your products and services. For example, a non-alcoholic beer that tastes bad versus one that tastes good.Customer Perceptions
Negative customer perceptions such as a technology brand that is associated with a legacy technology such that the brand sounds outdated to many customers in its target market.Positioning
The valuable uniqueness of your products relative to the competition. For example, an organic coffee product that has nothing special about it as compared to the other product's on the shelves of supermarkets.Target Market
Competitive weaknesses related to your target market such as a demographic that is shrinking. For example, a sporting goods company that is heavily associated with a sport that is less popular with younger generations.Productivity
The productivity of your employees. For example, a graphics design shop that consumes an employee month to deliver a logo when a competitor delivers logos of similar value with less than a week of effort.Technology
The systems and applications you use and their impact on things such as productivity, efficiency, customer satisfaction, cost and the turnaround time of processes. For example, an aging technology company that uses systems that are more costly to maintain and difficult to use than the competition.Information Security
Information security vulnerabilities such as employees who are unaware of basic defensive computing techniques.Infrastructure
Infrastructure are basic services such as an internet connection or road. For example, a wholesaler located in a remote location on a road that is prone to traffic jams may have a competitive disadvantage to a wholesaler located near a major port with significant transportation infrastructure in the area.People & Planet
The negative impacts of your business on the environment and communities in which you operate or sell. For example, an industry that produces $4 billion in economic goods but costs society $400 billion in economic bads might reasonably expect that they will eventually be regulated or asked to pay these costs.Organizational Culture
Organizational culture issues such as resistance to change.Innovation
The capability to change and to develop new value that is non-obvious. For example, a technology company that is often trying to copy the competition as opposed to doing anything that creates new types of products, markets and business models.Partnerships
Weaknesses of partners or relationships with partners. For example, a manufacturer of air conditioning units has a large number of quality control failures due to low quality parts from a supplier.Finances
The financial position of a business. For example, an electric car manufacturer with a large debt that will have difficulty refinancing this debt if financial conditions tighten.Processes
Business processes that fall behind the competition. For example, a university that takes a minimum of 6 months to recruit a professor when the competition can do it in 2 months. This may lead to talent flowing to competing institutions.Concentration
Concentration risk such as a farmer who only produces one commodity crop such that they are vulnerable to price swings.Barriers to Entry
A firm with a successful business model, product or service that is easily challenged by newcomers. For example, a small electric bus company that produces innovative vehicle models that are easily emulated by far larger competitors with more mature manufacturing capabilities.Business Model
A flawed business model such as a company that is able to grow revenue but is not able to become profitable. This typically occurs because growth was fueled by the company offering value that exceeded price with no ability to obtain a price that's higher than cost.Reputation
A poor reputation due to factors such as leadership, ethics and quality.| Overview: Weaknesses (SWOT) | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Competitive disadvantages in the current environment. | |
Related Concepts | ||










































