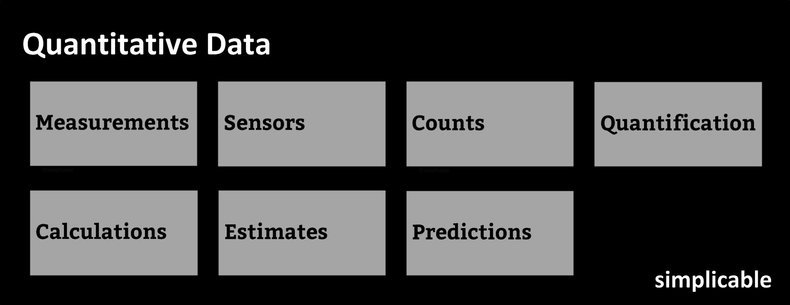
Measurements
A measurement of something physical. For example, a food safety inspection that measures the temperature of food stored in a restaurant refrigerator.Sensors
Sensors are devices that automatically measure the physical world to create streams of data. For example, a digital camera turns electromagnetic radiation into a series of numbers using a color model.Counts
Counting things. For example, a train station that counts the number of passengers who enter the station in real time.Quantification
Converting qualitative human judgements into numbers. For example, asking customers to rate their satisfaction on a scale of 1 to 4.Calculations
Mathematical calculations such as calculating gross margin based on monthly sales figures.Estimates
Producing numerical estimates as opposed to exact calculations using algorithms, artificial intelligence, business rules or human judgement. For example, a garbage sorting robot may estimate the probability that a particular object is recyclable plastic.Predictions
Predictions produced by algorithms, artificial intelligence or people. For example, a stock analyst may predict the future revenue and net earnings of a company.| Overview: Quantitative Data | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Data represented as numbers. | |
Related Concepts | ||