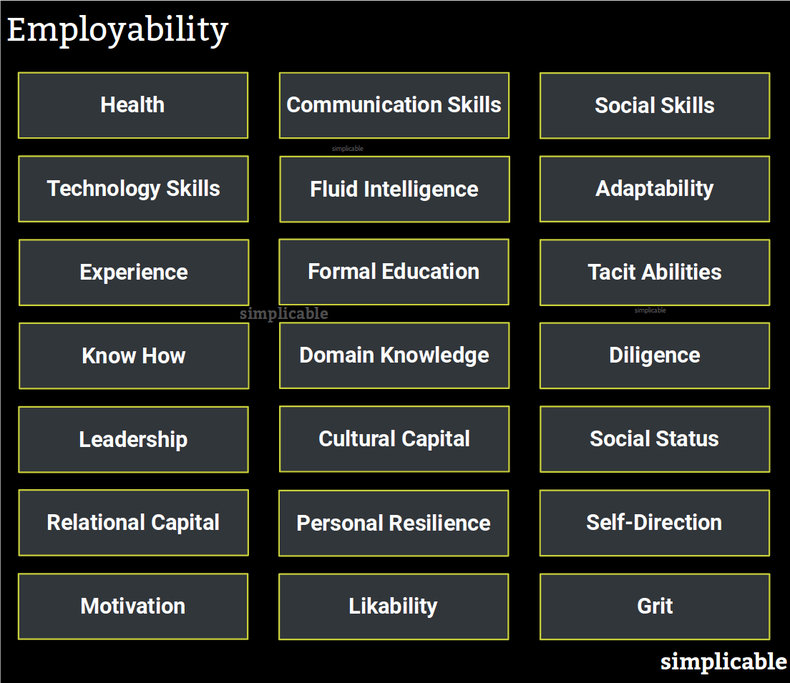
Health
The health of an individual as it relates to their ability to direct energies towards work.Communication Skills
Communication skills including business communications such as marketing, sales and stakeholder management abilities.Social Skills
Social skills including building rapport, influencing and collaboration.Technology Skills
An ability to be productive with the technologies an employer is using.Fluid Intelligence
Fluid intelligence is the capacity to learn new things and respond to novel situations in a reasonable way.Adaptability
A willingness and ability to change. For example, an experienced employee who is able to quickly adapt to a new corporate culture.Experience
An individual's experience in a profession or life in general. Individuals tend to make mistakes early in a career, learn from these mistakes and improve such that experienced individuals are often productive.Formal Education
Formal education can provide a foundational knowledge that is not easily gained through self-study or experience. For example, a computer science program that teaches first principles of computing such as computational complexity that may not be obvious from working on code or scripts in a professional setting.Tacit Abilities
Talents that can't be easily acquired or taught. For example, an executive with a long history of making good decisions that produced superior return on invested capital.Know How
Practical knowledge that can be applied to producing value. For example, a technician who knows how to fix an elevator.Domain Knowledge
Knowledge of a subject, profession or industry. For example, a software developer who has broad knowledge of the investment banking industry.Diligence
Diligence is the ability to apply your full concentration even if you aren't feeling motivated.Leadership
Leadership is the ability to get people moving in the same direction.Cultural Capital
Cultural capital is the ability to influence in the context of a culture. For example, a boat salesperson who is fully immersed in sailing culture.Social Status
An individual's reputation and how they are perceived by others. For example, an individual who is perceived as fashionable and cool who easily gets job offers from fashion retailers.Relational Capital
An individual's professional network such as a salesperson who knows a large number of people in an industry.Personal Resilience
Personal resilience is the ability to endure stress without a loss of productivity. For example, a cabin attendant who remains professional and helpful in severe turbulence.Self-Direction
Self-direction is the ability to set goals, handle problems, make decisions and navigate uncertainty without direction from others.Motivation
It isn't fun to hire and manage someone who wants to be somewhere else. As such, motivation for a role makes an employee more employable. For example, front desk staff at a hotel who truly enjoy their role and view it as important as opposed to viewing it as below their talents.Likability
In many cases, employers will hire the candidate they find most likable.Grit
In some roles, employers value grit such as a willingness to challenge others and high tolerance for disagreement.| Overview: Employability | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The value offered by an employee to employers. | |
Related Concepts | ||