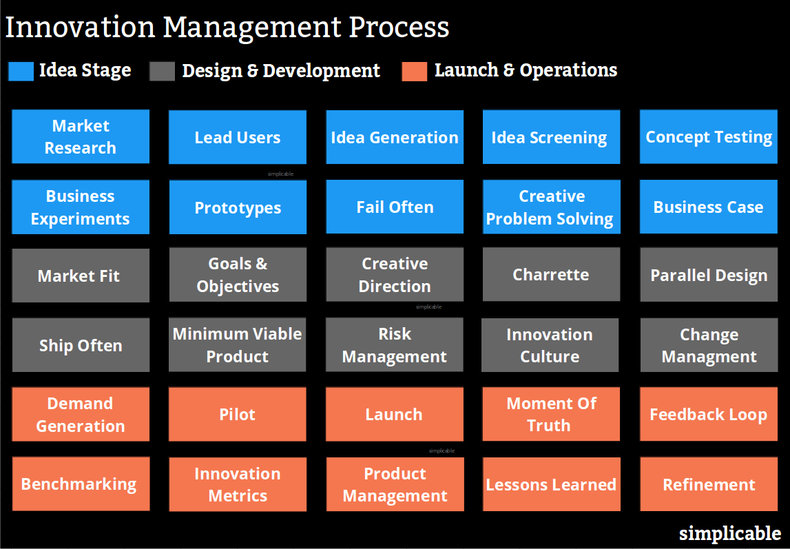
Idea Stage
Generating a large number of creative ideas and validating until your left with your best ideas that are documented as a business case.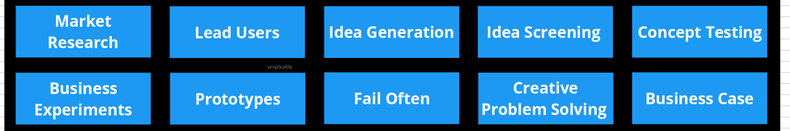
Market Research
Innovation teams are expected to be well-versed in the current market including customers, competitors, product culture, technology and industry trends.Lead Users
Engaging the users who are pushing your products to their limits.Idea Generation
The optimistic process of generating creative ideas.Idea Screening
Idea generation and screening are separated into completely different activities that require a different frame of mind. Idea screening is more of a pessimistic process of filtering ideas that are likely to fail until you are left with your best ideas.Concept Testing
Testing ideas at the conceptual level. For example, pitching product ideas to lead users with a poster.Business Experiments
Validating your best ideas by developing experiments that will produce useful data.Prototypes
Developing partial implementations to test ideas.Fail Often
Innovation management may track the number of failures in a period as a positive metric. For example, a firm that generates ten ideas and implements ten ideas might be unlikely to innovate as compared with a firm that tests thousands of ideas and implements ten.Creative Problem Solving
The process of problem solving to fix failures. Innovation is associated with allowing things to fail. However, it is common to fix problems along the way, particularly for ideas that have high potential.Business Case
Documenting the value of your best ideas as a formal business case as a means of communication to support strategy and decision making.Design & Development
Implementing ideas in a lightweight and risk managed process that doesn't produce overly costly failures.
Market Fit
Developing strategies, goals and objectives in terms of customer needs, customer perceptions and the competitive environment.Goals & Objectives
Defining goals and objectives. This is often a backlog of things you'd like to achieve.Creative Direction
Design and development requires creative vision and direction.Charrette
A charrette is an intensive group process of producing design work.Parallel Design
Creating multiple designs for the same project in a competitive process.Ship Often
Implementing work in small chunks that are quickly put in front of customers. This typically involves creating a backlog of work that is prioritized for each development cycle.Minimum Viable Product
Identifying the minimum set of work that is required to operationalize a product.Risk Management
Identifying and managing risk. The more risk you take, the more important it is to manage it. As such, aggressive change and risk management aren't mutually opposed or inconsistent.Innovation Culture
Developing a culture where aggressive change is a norm and expectation. An innovation culture also requires a creative environment such that people bravely offer ideas as opposed to hiding in mediocrity.Change Management
The leadership of change.Launch & Operations
The process of launching, measuring and improving.
Demand Generation
The marketing process of generating demand for a product or service. Innovation can be particularly difficult to sell if it requires customers to change their habits and methods.Pilots
Launching on a limited basis to reduce risk and gain information for improvement.Launch
The commercial launch of innovations.Moment of Truth
A moment of truth is a type of customer interaction that is a strong indicators of the success of a product or service. For example, when customers first throw a new bowling ball or first need to return an item to an ecommerce seller.Feedback Loop
Establishing systems that allow your results to be measured to drive improvement or evaluate a pilot or product.Benchmarking
Comparing your results to your industry. If a product is truly innovative it represents a large improvement over the best results in an industry.Innovation Metrics
Metrics that are relevant to innovation such as time to market and time to volume.Product Management
Where innovation is successful, it soon requires traditional product management processes such as identifying and managing competitive threats.Lessons Learned
Where products fail, there is an effort to learn from failure to recover value such as knowledge. In some cases, a failed product points the way to a new idea that is far more valuable.Refinement
Where innovation launches a minimum viable product that is shown to be valuable it often makes sense to rapidly improve quality.| Overview: Innovation Management Process | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The process of managing programs of creativity, experimentation and aggressive change. | |
Related Concepts | ||