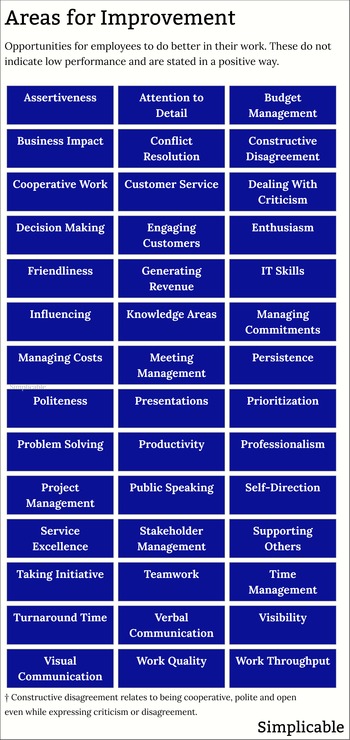
Avoiding action items | Building relationships & trust |
Conflict resolution | Decision making |
Documentation & record-keeping | Email etiquette |
Follow-through | Following policies & processes |
Formal communication | Handling criticism |
Handling difficult customers | Inattention to detail |
Industry knowledge | Inflexibility |
Interpersonal conflict | Lack of assertiveness |
Lack of ownership | Lack of initiative |
Language skills | Leadership skills |
Low commitment | Management skills |
Managing commitments | Managing remote work |
Meeting management | Negotiation |
Organizational skills | Organizational visibility |
Overanalyzing | Overcommitment |
Perfectionism | Presentation skills |
Prioritization | Problem solving |
Product knowledge | Productivity |
Professionalism | Project management |
Public speaking | Punctuality |
Quality of analysis | Setting expectations |
Stress management | Teamwork issues |
Technical know-how | Time estimation |
Time management | Unresponsiveness |
Work quality | Written communication |
Public Speaking
Fear of public speaking or a general lack of experience in front of a crowd.Presentations
Communicating information in smaller settings such as a meeting.Workload Management
Taking on too much. For example, being pushed by a vocal stakeholder to take on commitments that are essentially impossible to achieve.Prioritization
Mistakes of prioritization such as perfectionism whereby you spend too long improving something.Stakeholder Management
Failing to manage commitments or the expectations of your stakeholders.Technical Skills
A technical skill that you're trying to improve such as scripting.Hard Skills
Hard skills are anything that are easy to validate with a standard test. For example, accounting knowledge. These are excellent weaknesses if you want to communicate a desire for education, training and self-learning.Know-how
Specific knowledge that you need to develop. For example, an elevator technician who doesn't know how to repair a particular brand or model.Industry Knowledge
Entering a new industry where you have little experience. For example, a telecom professional who transitions to banking.Language
Language skills such as a second language that is required for a role.People Skills
People skills such as maintaining a friendly demeanor towards customers.Leadership
Leadership challenges such as defeating resistance to change.Management
Inexperience with management or some shortfall regarding the direction and control of teams.Project Management
Planning and controlling projects. For example, a software developer who wants to communicate to an employer that they aren't capable nor interested in project management.Organization
Some organization skill or habit that you're trying to improve such as taking detailed meeting minutes.Processes
Being too strict and rigid with respect to internal controls. The opposite weakness would be ignoring important controls and applying ad hoc processes where formal processes are better.Knowledge Management
Knowledge management issues such as a failure to capture useful documentation.Competition
Being overly competitive or not competitive enough. For example, a salesperson who allows a peer to take over in meetings.Influencing
Influencing such as communicating your wins and value to management.Communication
Communication issues such as being too direct or not direct enough.Difficult Conversations
Difficult conversations such as a manager who has trouble talking to an employee about their poor personal hygiene.Emotional Intelligence
Perceiving the emotions of others and behaving accordingly. For example, a manager who fails to see how strongly an employee feels about something.Customer Service
Customer service challenges such as dealing with difficult customers.Productivity
Productivity issues such as problems managing meetings to be brief and useful.Work Quality
The quality of your deliverables. For example, a software developer who tends to deliver buggy code.Adaptability
A tendency to resist change or a failure to adapt to change. For example, a software developer who wants to use their favorite old technology for everything who resists new approaches.Risk Taking
Too much or too little risk taking. For example, a team manager who fails to produce brave initiatives but seeks only safety and comfort for their team.Tolerance for Disagreement
An inability to engage in debate and creative tension without becoming overly emotional.Personal Resilience
Problems dealing with stress and failure such as taking criticism too personally.Types
The following are common types of professional weakness.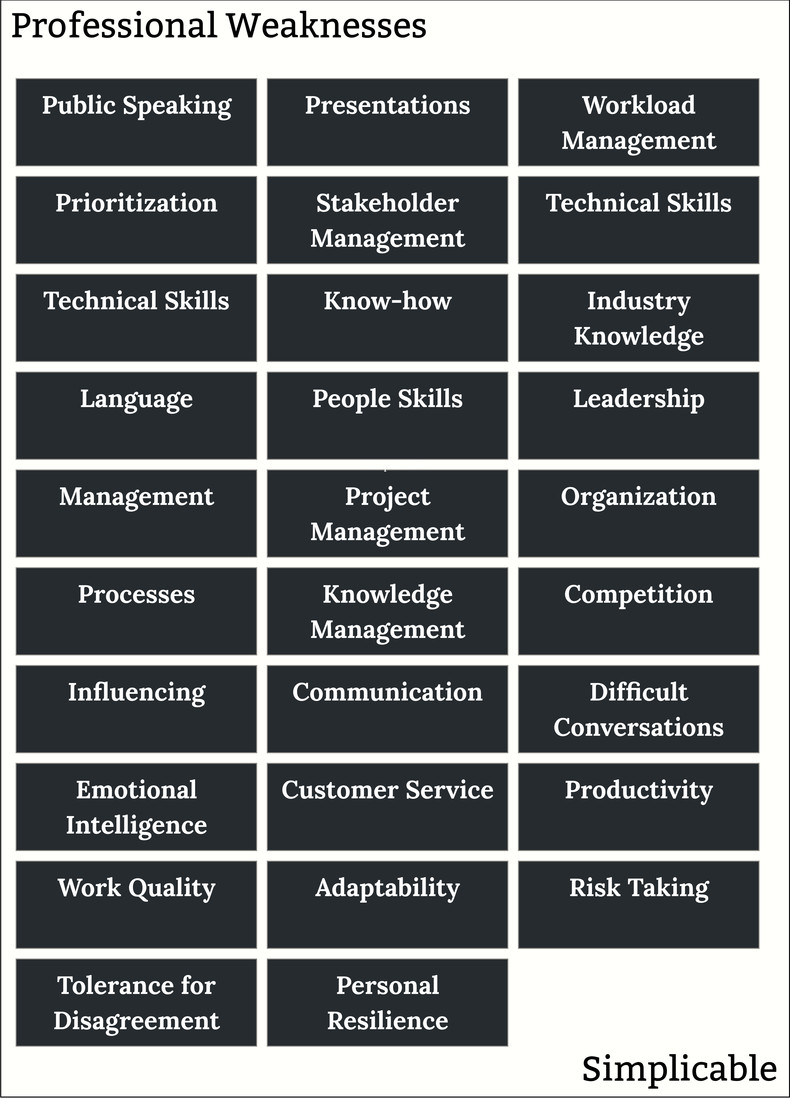
Answering "What is your greatest weakness?"
When asked for your greatest professional weakness, it is advisable to avoid highlighting debilitating weaknesses while showing self-awareness and a drive to self-improve.