Addresses
Addresses such as an IP address that are designed to locate digital resources. For example, the IPv6 address:2001:4860:4860:0:0:0:0:8888can be processed by networking equipment such as a router. The human readable equivalent of an IP address is a URL such as simplicable.com.Messages
Messages such as a web server that sends SSL encrypted HTTP messages to a web browser. The human readable equivalent is the web page rendered by the web browser.Files
Most files are designed to be machine readable with the exception of text files. For example, a digital camera that creates image files that can be processed by a wide range of information technologies such as image viewers and editors.Databases
Databases are systems that structure large collections of information to be read and updated efficiently by machine.Bar Codes
Bar codes such as a product label that can be scanned by a point of purchase device.Optical Character Recognition
In some cases, printed materials are designed to be read by machine with an id or other data that is meaningless to people. For example, a drivers license may have a short segment of printed text can be read with optical character recognition to pull up a database record.Magnetic Stripe
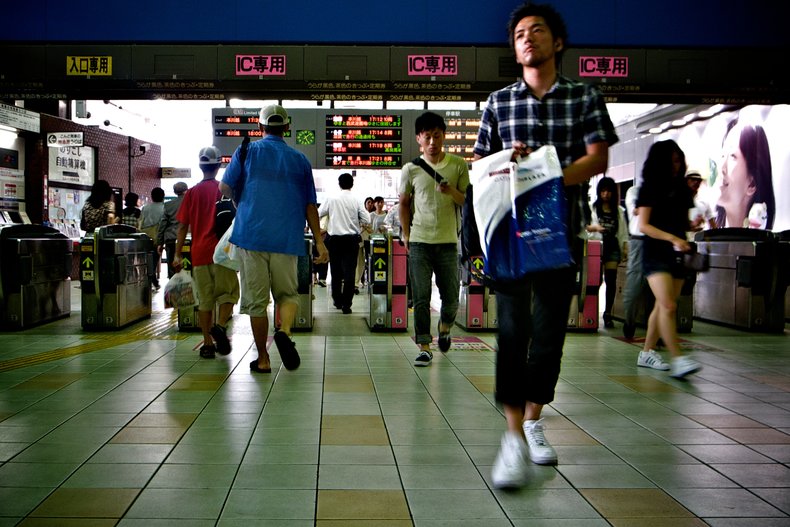
Magnetic stripes that encode digital data such as an train ticket that can be read by an automated ticket gate.Near Field Communication
Low power technologies for communicating information to nearby devices. For example, an RFID tag embedded in a shirt that can communicate an identifier to readers. This may be used for inventory management, checkout scanning and loss prevention. It is a good practice to remove such tags from items when they are purchased by a customer.Wireless Communication
Short distant wireless communications that have a greater range than near field communication and require more power. For example, a game controller that communicates to a game console using bluetooth wireless technology.Multiple Formats
In some cases, a physical thing will use multiple techniques to communication data to machines. This can be done for compatibility reasons or for security. For example, a passport might have a bar code and embedded RFID device. These may use cryptographic techniques to make them difficult to forge or misuse. The information embedded in a passport varies by country but can include your photograph, name, gender and date of birth. Some countries may embedded additional biometric information such as images of your fingerprints.| Overview: Machine Readable | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A digital or physical entity that is designed to communicate information to technology. | |
Related Concepts | ||