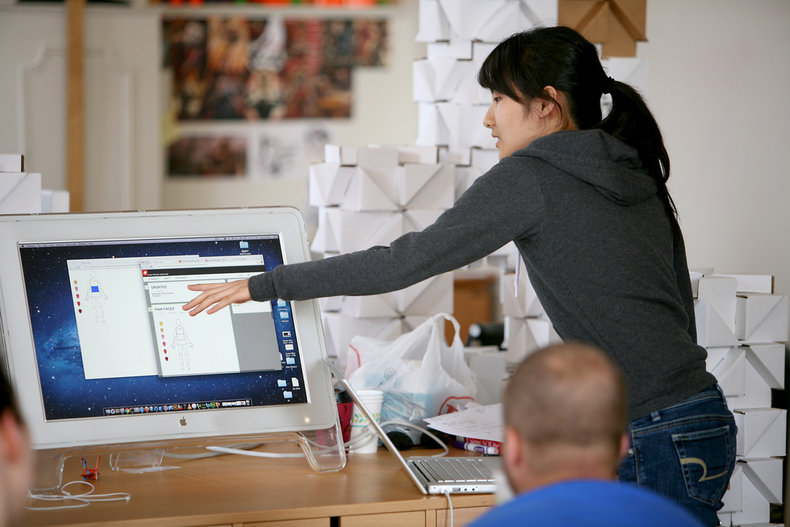
Users
Interaction design is all about people. This includes thought processes, needs, expectations and perceptions. As such, it is considered naive to design interactions without being fully engaged with users. This can be superficially solved with abstractions such as user personas. It is far better to be engaged with users and immersed in the culture surrounding your products.Human Factors
Human factors are the physical, cognitive and behavioral characteristics of people. This is commonly applied to interaction design to ensure interfaces are useful for as many people as possible. For example, human factors is used to model the needs of people with disabilities to ensure designs are universally accessible.User Interfaces
The design of tools and environments that can be controlled and/or explored by people. User interfaces may be designed to be productive and pleasing to use such that controls feel intuitive and environments are either stimulating or relaxing.Sensory Design
Designing for the senses including visual design, look and feel, product form and other experiences of sight, sound, touch, taste, smell and sensation.Information Architecture
The structural design of information environments. This is typically intended to organize complex and rich information resources into manageable units that are easy to explore.Information Design
The design of information itself including media, text, game content, documents and software interfaces. Information design is about communicating effectively whereas information architecture is about making information easy to find.Technology
The design of technology for user interaction. Most interaction designers work with commercially available technologies. However, some are engaged in the research, development and commercialization of new technologies for user interfaces or environments.| Overview: Interaction Design | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | The design of environments that people use. | |
Definition (2) | The practice of designing user interfaces for products, services and tools. | |
Related Concepts | ||