No Exceptions
A bright line rule is not open to exceptions. For example, the rule that requires law enforcement to inform suspects of certain rights before being interrogated was interpreted as a bright line rule in a landmark decision known as Miranda v. Arizona by the United States Supreme Court. The reading of these rights to suspects became known as a Miranda warning. According to the ruling, this must be done without exception before an interrogation.Unambiguous
A bright line rule is well defined to be completely unambiguous. For example, an individual who has a rule that they never drink alcohol, whatever the occasion.Unbalanced
It is difficult to make a rule both completely unambiguous and balanced such that it considers a large number of potential situations. For example, a firm that establishes a bright line rule that any salesperson who doesn't meet quota can not be rated higher than "unsatisfactory" on their performance review without exception. This rule does not allow for balance with extenuating circumstances such as sickness, poor economic conditions or product failures that are beyond the salesperson's control. Applying this unbalanced rule may result in the loss of high performing talent who simply had bad luck in a particular quarter.Grey Areas
Bright line rules lend themselves to black and white thinking that views the world as right and wrong, good and bad, talented and untalented, pass and fail, advantaged and disadvantaged, true and false. For example, a credit card application that automatically rejects all self-employed individuals without considering their income, wealth and reputation. The realities of life tend to be complex with degrees of truth such that overly simplistic bright line rules can be unfair and suboptimal.Control
Bright line rules may allow for centralized control of processes, practices and procedures as it doesn't allow front line employees to use any judgement in applying rules.Automation
Bright line rules are far easier to automate than systems that require handling of grey areas. For example, a system that automatically sends a ticket to anyone who speeds anywhere, anytime without exception would be easier to automate than a system that only tickets drivers who take unreasonable risks on the road. Historically, automation has lead to the replacement of flexible systems of human judgement with concrete rules that are never broken. This may change as more advanced systems such as artificial intelligence and fuzzy logic can handle grey areas.Trust
Bright line rules may be designed to remove the power of someone you don't trust. For example, an airline that designs rules with no exceptions because they don't trust their employees to apply such exceptions. In some cases, an individual establishes bright line rules for themselves because they don't trust their own judgment. For example, a person on a diet who sets bright line rules for what they can and can't eat.Values
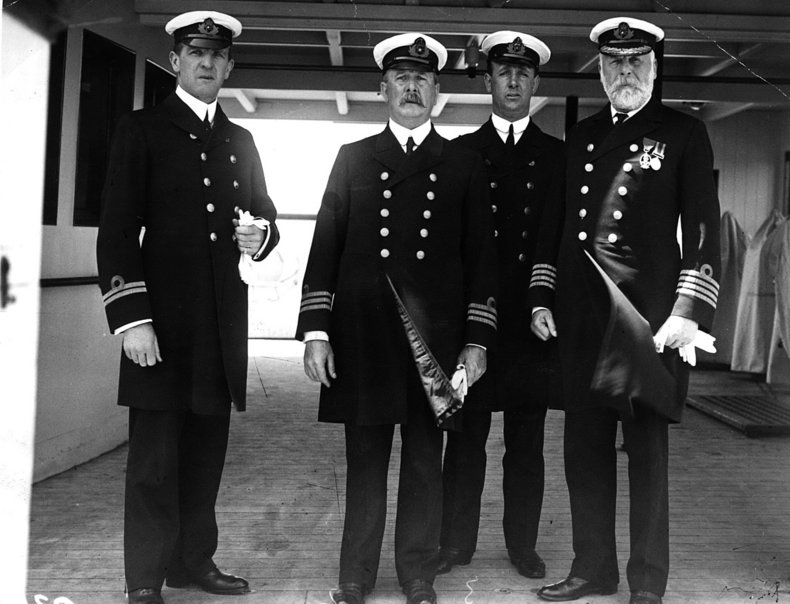
Bright line rules are often used to prioritize a principle that must be upheld in the most difficult of circumstances without exception. For example, the tradition that a "captain goes down with the ship" is a bright line rule that a captain is not allowed to leave a vessel in peril under any circumstances until they have made every possible effort to save the lives of passengers. Taken literally, the captain is not supposed to survive unless all passengers survive or the vessel itself remains afloat.Notes
A fine line rule is also known as a balancing test or balancing rule.Photo above: Captain Edward Smith (right) who went down with the Titanic.| Overview: Bright Line | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A law, regulation, rule or test that isn't open to interpretation, judgment or exceptions. | |
Related Concepts | ||