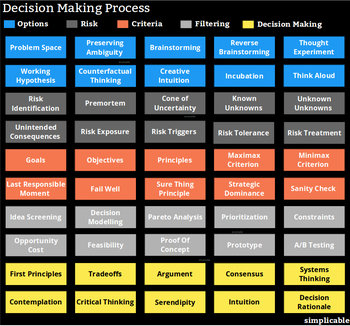
Overview
Problem statements are generally concise with great attention paid to wording. Slight differences in your problem statement can lead to completely different solutions. A well designed problem statement can improve the problem solving processes and produce more desirable outcomes.Resets
If problem solving stalls or produces poor solutions it is common to revisit the problem statement. In theory, a new problem statement can spark completely new insights.Open-ended
An open-ended problem statement sets no constraints or conditions. This allows for creativity in problem solving as the solution space is large. For example, the problem statement "develop a new product that addresses a significant customer need."Closed-ended
A closed-ended problem statement imposes constraints and conditions. This is used to limit the solution to those that fulfill your goals. For example, "develop a bicycle helmet that will generate sales of $100 million a year with profit margins over 50%."| Overview: Problem Statement | ||
Function | ||
Value | A well designed problem statement may lead to faster and higher quality solutions to problems. | |
Common Pitfalls | Solving the wrong problem.Complex problem statements that make the problem solving process difficult.Failure to properly validate and challenge a problem statement. | |