
Products
At the highest level, the production of a product typically has the following value chain.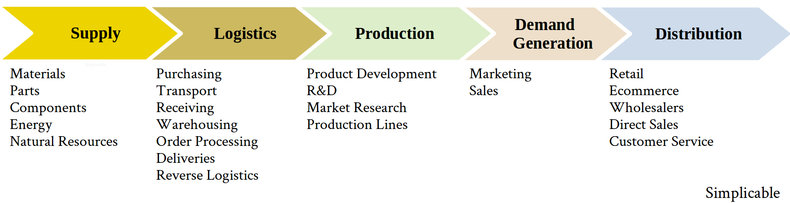
Inputs required to make the product such as materials, components, parts, energy and natural resources. | |
Processes of supply and fulfillment of orders including procurement, warehousing, transportation, distribution, reverse logistics and field service. | |
The development and manufacturer of products. It is also common to separate product development as a separate value added step. | |
The process of selling the product including all marketing and sales activities. | |
The process of reaching the customer to deliver your obligations to them. |
Services
Services are based on various layers of intangible value.
Inputs including energy, equipment and physical elements of a service, known as service tangibles, such as the food served by a restaurant. | |
Service Delivery | The operational work of delivering a service such as the logistics and kitchen operations of a restaurant. In many cases, information technology is viewed as a value added part of the service. For example, an airline would have no value without its systems for managing bookings, flights and other aspects of operations. |
Marketing & Sales | The process of developing, branding, distributing, promoting, pricing and selling services. |
Any touchpoints with the customer in the end-to-end customer experience adds value. |
Ecommerce
The ecommerce value chain for sales of physical products. This differs from other ecommerce models such as Software as a Service.
Supply | In some cases, a manufacturer or service provider sell their own goods by an ecommerce channel. In this case, they add value at the supply level. |
Inbound Logistics | The process of purchasing goods, processing inbound deliveries and warehousing goods. |
The promotion, pricing and sales of goods using ecommerce channels or retail shops using a bricks and clicks model. | |
Outbound Logistics | The process of assembling the order and delivering it to the customer. |
Handling customer inquiries and requests such as returns. |
Software as a Service
Software as a Service, or SaaS, is a business model that offers software that is hosted on a cloud platform. This allows customers to access scalable software without investing in data centers, hardware and software installations. The value chain for SaaS is mostly about technology with a thin layer of marketing and customer service. Some SaaS products sell themselves with word of mouth while others employ large global sales teams.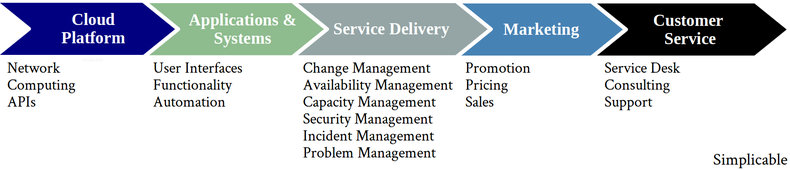
Cloud Platform | Foundational infrastructure and software services including the management of data centers. |
Applications & Systems | Applications and systems for end-customers. |
The operations of applications, systems and cloud platforms for high availability. This is often highly automated and includes an escalation process for incidents and problems. | |
Promotion, pricing and sales. Software as a service may be sold by a global sales team using personal selling methods. Alternatively, there may be an attempt to automate this layer of the value chain too with a combination of digital advertising and ecommerce capabilities. | |
Customer Service | SaaS firms may offer multiple levels of customer service with self-service tools at the lowest price level progressing to a personal account representative that you can get on the phone. In some cases, SaaS is sold with support for customization via a consulting practice that adds another layer of value. |
| Overview: Value Chain | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A sequence of activities that each adds value to a product, service or experience. | |
Related Concepts | ||





































