
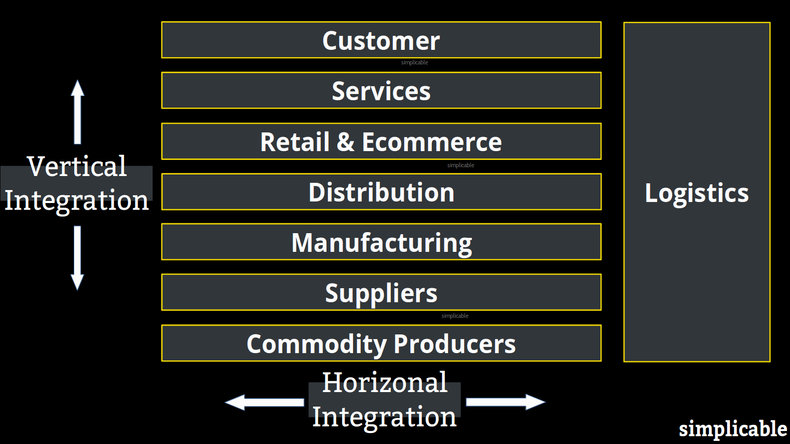
1. Commodities
An apple farmer begins to produce apple pies to move further up the value chain.2. Suppliers
A supplier of computer parts begins to manufacture finished goods such as mobile devices.3. Manufacturing
A manufacturer produces its own commodities and supply of parts. For example, a solar panel manufacturer that produces silicon, silicon wafers, solar cells and solar modules. This might be done to produce panels of superior quality to establish a competitive advantage.4. Wholesaling
A manufacturer may establish its own wholesale network in order to reach customers or retailers directly without a middleman.5. Direct to Customer
A tea farmer cuts out multiple levels of supply chain intermediaries by selling directly to customers from a website.6. Retailing
A fashion manufacturer opens its own retail shops to build brand recognition and control its brand experience.7. Logistics
An ecommerce firm begins deliveries to the customer to reduce dependence on delivery companies.8. Services
A bicycle manufacturer starts a bicycle rental service.9. End-to-End
A diamond company controls its entire supply chain including mining, logistics, manufacturing and retail.Advantages
Vertical integration can have several advantages for a firm:QualityControlling the end-to-end quality of your products and services. CostReducing costs by cutting out intermediaries in the supply chain such as wholesalers.Risk ReductionRemoving risks such as unreliable supply chain partners. For example, an ecommerce company that is able to replace a delivery partner that is often delivering things late and losing packages.Competitive AdvantageBuilding competitive advantages such as a firm that achieves higher quality products and services than all competitors by controlling every detail of the supply chain. For example, a jam company that produces a higher quality jam by farming higher quality berries.Disadvantages
Vertical integration has several potential disadvantages for a firm:FlexibilityVertical integration tends to be a more rigid structure that is more difficult to change than a situation where you have partnerships in the supply chain. For example, a jam company that grows its own strawberries and raspberries may have difficulty shifting to changing consumer tastes such as a preference for pomegranate and cherries. In other words, partners can be replaced quickly but your own organization can be difficult and expensive to change.Competitive AdvantageA firm does well to stick to areas where it has a competitive advantage. For example, an ecommerce company may be good at marketing and digital retailing but terrible at running a delivery company. In other words, they may intend to reduce costs and improve quality only to see higher costs and less quality due to their lack of capabilities in an area outside their experience.Anti-competitive PracticesVertical integration is often done in order to exclude competitors from an industry. For example, if you own all the parts suppliers for a particular product, it is far more difficult for a competitor to challenge you. This is a negative aspect of vertical integration for society as it can allow a firm to dominate an industry. This can result in higher prices and lower quality.Vertical Integration vs Horizontal Integration
Vertical integration is a move to control more of your supply chain for a single product or product category. Horizontal integration is the expansion of activities at the same level of the supply chain such as a chain of coffee shops that launches a chain of restaurants. These two strategies aren't mutually exclusive and both can be pursued at the same time.Forward Integration vs Backward Integration
Forward integration is vertical integration that moves up the supply chain in the direction of the customer such as a manufacturer that opens retail locations. Backward integration is vertical integration that moves down the supply chain in the opposite direction of the customer such as a retailer that begins manufacturing its own products.| Overview: Vertical Integration | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A firm that owns multiple levels of its supply chain. | |
Related Concepts | ||
































