
Working Conditions
The working conditions at a firm such as overtime hours or work from home policies.Tone At The Top
The example set by executive management that tends to impact behavior at every level of a firm. For example, if executive managers demonstrate respect for customers this may influence others to do the same.Leadership
Leadership is the ability to influence both with and without formal authority. For example, a technical visionary at a firm that everyone respects such that they can defeat ideas they view as flawed.Organizational Structure
The formal structure of an organization as represented in an org chart that indicates reporting lines and authority levels.Employees
Each position in an org chart is filled with a person who has a personality, character, world view, habits, talents and set of relationships within the organization.Performance Management
Performance management is the process that aligns work and behavior to objectives. For example, a customer service team that can get away with being rude to customers versus a team where this would be quickly detected as low performance.Organizational Culture
The shared values, norms, habits, expectations, symbols, stories, mission and vision of an organization that is formed through shared experience over time.Relationships
The relationships that exist within a firm represents a power structure that is undocumented.Processes
The formal business processes of the organization.Systems
The systems in place that must be used to accomplish things.Internal Controls
Internal controls such as budget controls and project reviews that are required to get anything done.Organizational Climate
The prevailing attitude at a firm such as an environment of aggressive change and competition versus a firm where people resist change and avoid competitive battles.Office Politics
The way that power is distributed and decisions are made in a firm.Resources
The resources available such as budget or office space.Capabilities
The business capabilities of a firm such as a company with mature project management capabilities that can manage complex projects in a reasonable way.Know-how
Practical knowledge that exists within the organization. For example, a firm that is well-versed in information security.Talent
The talent of a single employee can have a large impact on a firm such as a director of product development who is always inventing winning products.Constraints
Limits to resources, systems, capabilities, culture and talent.Summary
The following are basic elements of the internal environment of an organization that may influence its performance and the employee experience.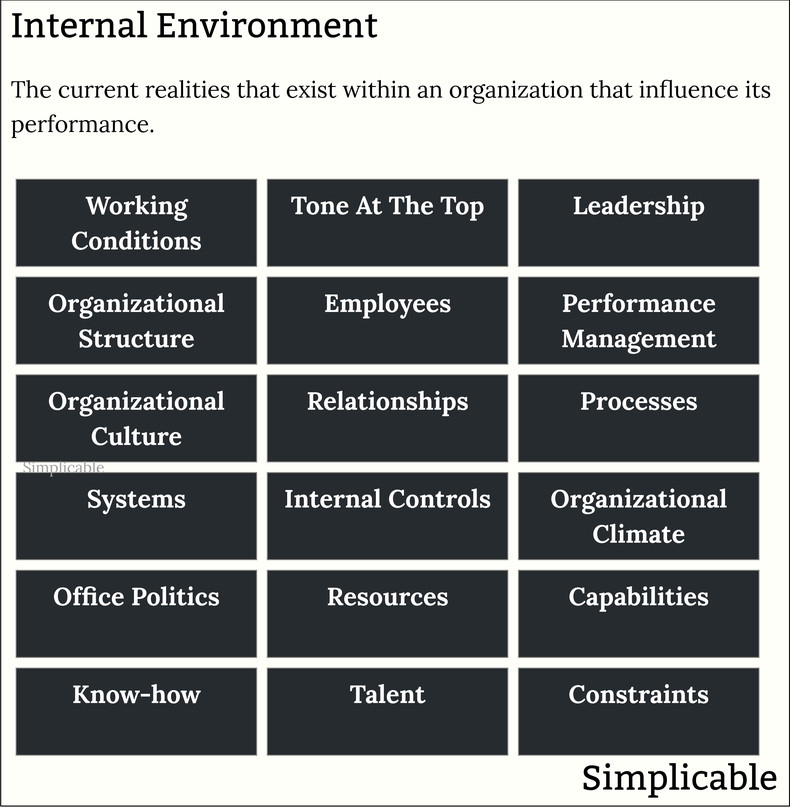
Overview
An overview of the internal environment and addition examples:
| Overview: Internal Environment | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The internal realities of an organization that influence productivity, efficiency, work quality, performance and strategy. | |
Related Concepts | ||




































